
Improve User Research Sprig to Success
Improve User Research Sprig: Let’s dive into how we can supercharge our user research game! This isn’t just about tweaking existing methods; it’s about a complete overhaul, from understanding the shortcomings of our current approaches to leveraging technology for deeper insights. We’ll explore innovative techniques, efficient workflows, and powerful data analysis strategies to transform how we gather and interpret user feedback.
This journey will cover everything from identifying common challenges in current user research practices to effectively communicating findings to stakeholders. We’ll look at specific examples of successful case studies and discuss the importance of continuous user research for ongoing product development. Get ready to level up your user research skills and unlock the true potential of user-centered design!
Understanding Current User Research Practices
User research is crucial for creating products and services that truly meet user needs. However, despite its importance, many organizations face significant challenges in effectively implementing and leveraging user research methodologies. This exploration delves into the common pitfalls, areas for improvement, and limitations within the current landscape of user research.
Common Challenges in User Research Methodologies
Many obstacles hinder effective user research. Resource constraints, such as limited budget and time, frequently lead to rushed studies with compromised data quality. Another common challenge is recruiting participants who accurately represent the target user base. Finding a truly representative sample can be difficult, leading to biased results and potentially flawed conclusions. Furthermore, the analysis of qualitative data, such as interview transcripts or open-ended survey responses, can be time-consuming and require specialized skills.
This often results in a bottleneck in the research process, delaying product development. Finally, effectively communicating research findings to stakeholders who may lack a user research background presents another significant hurdle.
Areas for Improvement in User Research Processes
Several key areas within existing user research processes warrant improvement. First, a greater emphasis on integrating user research throughout the entire product development lifecycle is needed, rather than treating it as a standalone phase. Continuous user feedback, incorporated iteratively, can significantly enhance product design and user experience. Second, improving the accessibility and usability of research tools and techniques is vital.
This includes simplifying data analysis processes and making them more accessible to researchers with varying levels of technical expertise. Third, a stronger focus on building a culture of user-centricity within organizations is essential. This requires training and education for all team members, emphasizing the value of user insights and fostering a collaborative approach to research.
Limitations of Current Tools and Techniques
While numerous user research tools and techniques exist, many limitations persist. For example, relying solely on quantitative methods, such as surveys, can provide a superficial understanding of user behavior, neglecting the nuances of individual experiences and motivations. Conversely, relying solely on qualitative methods, such as interviews, can be subjective and lack generalizability. Moreover, many existing tools lack robust capabilities for integrating and analyzing data from diverse sources, hindering a holistic understanding of user behavior.
The increasing complexity of digital products and services also poses a challenge, requiring researchers to adapt their methodologies and tools to account for diverse interaction contexts. For instance, the use of eye-tracking technology can provide valuable insights into user attention and engagement, but its cost and technical complexity limit its widespread adoption.
Comparison of User Research Methodologies and Their Effectiveness
Different user research methodologies offer varying strengths and weaknesses. A/B testing, for example, is highly effective for measuring the impact of specific design changes on user behavior, but provides limited insight into the underlying reasons behind those changes. Usability testing, on the other hand, allows researchers to observe users interacting with a product, providing rich qualitative data about their experiences and challenges.
However, usability testing can be time-consuming and expensive. Surveys are cost-effective for gathering large amounts of data quickly, but often lack depth and context. Ethnographic studies offer rich contextual understanding of user behavior in their natural settings, but require significant time and resources. The choice of methodology depends heavily on the research questions, available resources, and the desired level of detail.
For example, a startup with limited resources might prioritize surveys and A/B testing, while a large organization with ample resources might employ a mixed-methods approach, combining quantitative and qualitative methods for a more comprehensive understanding.
Enhancing Research Methods
Improving user research methodologies is crucial for creating products that truly meet user needs. A streamlined workflow, innovative data collection techniques, and a user-centric approach throughout the development lifecycle are key to success. This section explores strategies to enhance your user research process and maximize the impact of your findings.
A More Efficient User Research Workflow
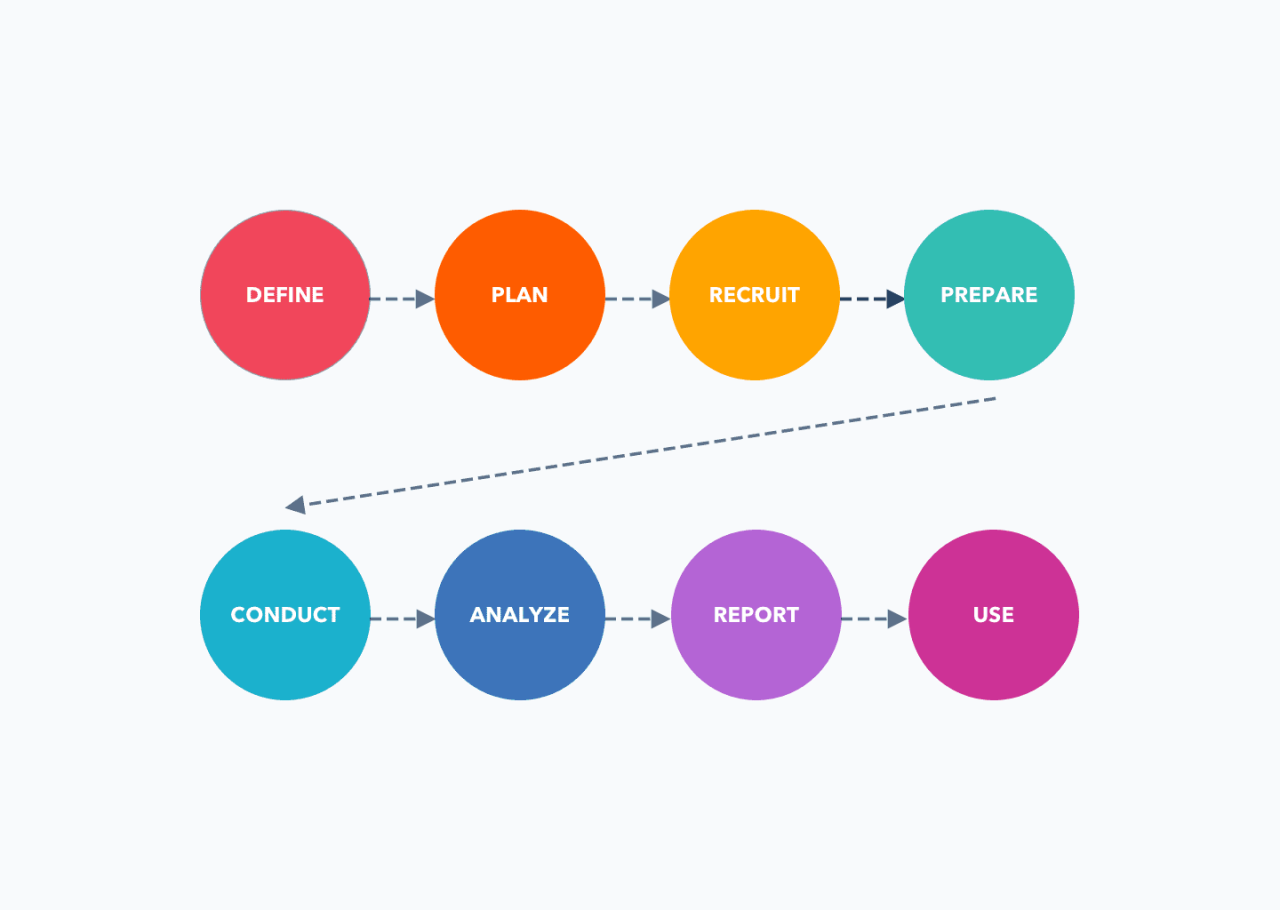
An efficient workflow minimizes wasted time and resources while ensuring comprehensive data collection. A well-structured approach should begin with clearly defined research objectives, followed by participant recruitment, data collection (using appropriate methods), analysis, and reporting. Using project management tools to track progress and deadlines is also beneficial. For example, a Kanban board can visually represent the stages of the research process, allowing for easy monitoring and adjustment.
Each stage should have defined deliverables and clear timelines, fostering accountability and ensuring the project stays on track. Regular check-ins with stakeholders are crucial for maintaining alignment and addressing any emerging issues.
Innovative User Research Methods
Beyond traditional methods like surveys and interviews, several innovative techniques can enrich data collection. Diary studies, for instance, provide rich longitudinal data by having participants record their experiences over a period of time. This offers valuable insights into user behavior in their natural environment. Another powerful method is ethnographic research, which involves observing users in their natural context to understand their behaviors and needs firsthand.
For example, observing how users interact with a product in their homes can reveal usability issues not apparent in a controlled lab setting. A/B testing allows for the comparison of different design iterations, providing quantifiable data on user preferences. By systematically testing variations, developers can identify the most effective design choices.
Best Practices for Conducting Effective User Interviews
Effective user interviews require careful planning and execution. Begin by developing a structured interview guide with open-ended questions that encourage detailed responses. It’s important to create a relaxed and comfortable atmosphere for participants, building rapport to encourage honest feedback. Active listening is crucial; interviewers should pay close attention to both verbal and nonverbal cues. Following a conversational style helps participants feel at ease and share more information.
After the interview, transcribing the recordings and carefully analyzing the data is essential for extracting meaningful insights. Thematic analysis can be employed to identify recurring patterns and themes within the interview data.
Incorporating User Feedback Throughout the Product Development Lifecycle, Improve user research sprig
User feedback shouldn’t be confined to a single phase of the development process. Instead, it should be integrated throughout, from initial concept development to final product launch and beyond. Early feedback helps refine the product vision and prevent costly mistakes later in the development cycle. Regular feedback loops, such as usability testing at different stages, allow for iterative improvements based on user insights.
This continuous feedback process fosters a user-centric approach, ensuring the product aligns with user needs and expectations. For example, incorporating user feedback during the prototyping phase can lead to significant design improvements, preventing costly rework later on.
A Structured Plan for Conducting Usability Testing
Usability testing involves observing users interacting with a product to identify usability issues. A structured plan begins with defining clear objectives and identifying key usability metrics. Recruiting representative participants is critical to ensure the test results are generalizable. A well-defined testing script should guide the testing session, ensuring consistency and efficient data collection. During the test, observers should document user actions, behaviors, and verbal feedback.
After the testing sessions, analyzing the data, identifying usability issues, and formulating recommendations for improvement are essential steps. This process should involve creating detailed reports with actionable insights to guide design improvements.
Improving your user research sprig means understanding your audience deeply. One fantastic way to gain those insights is by analyzing how people interact with your content on platforms like YouTube; check out this insightful guide on getting it on with YouTube to learn more about audience engagement. This data can then be directly applied to refining your research methods and ultimately creating a better user experience.
Leveraging Technology for Improved User Research
Technology has revolutionized user research, offering powerful tools to gather, analyze, and interpret data more efficiently and effectively than ever before. This allows researchers to gain deeper insights into user behavior, preferences, and needs, ultimately leading to better product design and improved user experiences. The ability to analyze large datasets quickly and identify trends that might be missed with manual methods is a significant advantage.
The Role of Technology in Data Analysis and Interpretation
Technology significantly enhances data analysis and interpretation by automating tedious tasks, providing sophisticated statistical analysis capabilities, and enabling the visualization of complex data sets. Software can quickly process large volumes of qualitative and quantitative data, identifying patterns and trends that might be missed through manual analysis. For example, sentiment analysis tools can automatically categorize user feedback as positive, negative, or neutral, providing a quick overview of overall user sentiment.
Furthermore, visualization tools can present complex data in easily digestible formats, such as charts and graphs, making it easier to identify key findings and communicate them to stakeholders. This allows researchers to move beyond simple descriptive statistics and delve into more nuanced analyses, revealing deeper insights into user behavior.
Suitable Software and Tools for Streamlining User Research
Several software and tools can streamline the user research process. For qualitative data analysis, tools like NVivo and Atlas.ti offer powerful features for coding, theming, and visualizing qualitative data from interviews, focus groups, and open-ended surveys. For quantitative data, statistical software packages such as SPSS and R provide advanced statistical analysis capabilities, enabling researchers to test hypotheses, identify correlations, and build predictive models.
User testing platforms like UserTesting.com and TryMyUI allow researchers to conduct remote usability testing efficiently, collecting video recordings and user feedback. Finally, project management tools like Trello and Asana can help organize and track the entire user research process, ensuring tasks are completed on time and within budget.
Utilizing User Research Data for Better Decision-Making
Effectively utilizing user research data is crucial for informed decision-making. The data should be used to identify user needs and pain points, validate design decisions, and measure the impact of design changes. For instance, findings from usability testing can inform design iterations, improving the user experience. Similarly, data from surveys can be used to prioritize features and functionalities based on user preferences.
By integrating user research data into the design process, organizations can create products and services that better meet user needs and achieve business objectives. A key aspect is translating research findings into actionable insights – identifying specific design changes or strategic shifts that address the discovered issues or opportunities.
A Step-by-Step Guide for Analyzing User Feedback with Technology
1. Data Collection
Gather user feedback through various methods (surveys, interviews, usability testing). Ensure data is properly labelled and organized.
2. Data Cleaning
Clean the data by removing duplicates, handling missing values, and correcting errors.
3. Data Transformation
Transform data into a suitable format for analysis. This may involve coding qualitative data or creating new variables from existing ones.
4. Data Analysis
Use appropriate software (e.g., SPSS, NVivo) to analyze the data. This might involve descriptive statistics, correlation analysis, or thematic analysis.
5. Data Visualization
Visualize the findings using charts, graphs, and other visual aids to effectively communicate the results.
6. Interpretation and Reporting
Interpret the findings in the context of the research objectives and create a comprehensive report summarizing the key findings and recommendations.
Comparison of Data Analysis Tools
| Tool | Qualitative Analysis Capabilities | Quantitative Analysis Capabilities | Collaboration Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| NVivo | Excellent; robust coding, theming, and visualization features | Limited; primarily focused on qualitative data | Good; allows multiple users to collaborate on projects |
| Atlas.ti | Excellent; similar capabilities to NVivo | Limited; primarily focused on qualitative data | Good; allows for collaborative research |
| SPSS | Limited; better suited for quantitative data | Excellent; wide range of statistical analysis tools | Moderate; collaboration features are available but not as extensive as some other tools |
| R | Moderate; with appropriate packages | Excellent; highly flexible and customizable statistical analysis capabilities | Good; supports collaborative coding and sharing of scripts |
Improving Data Analysis and Interpretation: Improve User Research Sprig
Source: danolsavsky.com
User research, regardless of the methods employed, generates a wealth of data. The true value, however, lies not in the data itself, but in our ability to analyze it effectively, interpret the findings, and translate them into actionable insights that drive design and business decisions. This section explores various techniques for analyzing both qualitative and quantitative data, visualizing findings, extracting actionable insights, and effectively communicating these insights to stakeholders.
Qualitative Data Analysis Methods
Qualitative data, often rich with narrative and context, requires careful analysis to uncover underlying themes and patterns. Several methods can be employed, each offering a unique perspective. Thematic analysis, for example, involves identifying recurring themes and patterns within the data. This could involve coding individual responses to identify s and concepts, grouping similar codes into themes, and then reviewing the themes to refine and confirm their meaning.
Another approach is grounded theory, which aims to develop a theory grounded in the data itself, emerging inductively from the analysis process. This method is iterative, with constant comparison of data points to refine and develop the theory. Finally, content analysis offers a systematic approach to quantifying the presence of specific words, phrases, or concepts within the data, enabling a more structured approach to qualitative data analysis.
Quantitative Data Analysis Methods
Quantitative data, typically numerical, offers a different lens for understanding user behavior. Descriptive statistics, including measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode) and dispersion (standard deviation, range), provide a summary of the data’s characteristics. Inferential statistics allow us to draw conclusions about a larger population based on a sample of data, using techniques like t-tests or ANOVA to compare groups or correlations to examine relationships between variables.
For example, we might use a t-test to compare user satisfaction scores between two different design prototypes. Regression analysis can help to model relationships between variables, allowing us to predict outcomes based on certain inputs.
Visualizing and Presenting User Research Findings
Effective visualization is crucial for communicating complex findings clearly and concisely. Charts and graphs, such as bar charts, pie charts, line graphs, and scatter plots, are valuable for presenting quantitative data. For example, a bar chart could compare the usage frequency of different app features. For qualitative data, word clouds, affinity diagrams, and thematic maps can effectively illustrate key themes and patterns.
An affinity diagram visually organizes related ideas, while a thematic map illustrates the relationships between different themes. Interactive dashboards can be particularly useful for presenting complex data sets, allowing stakeholders to explore the data at their own pace.
Identifying Actionable Insights from User Research Data
The goal of user research is to generate actionable insights that directly inform design and business decisions. This requires moving beyond simply describing the data to identifying the “so what?” – the implications of the findings. For example, if user testing reveals that a particular feature is confusing, the actionable insight would be to redesign the feature for improved clarity.
Prioritizing insights based on their impact and feasibility is also crucial. A framework like a prioritization matrix can help to systematically evaluate and rank insights based on these criteria.
Communicating User Research Findings to Stakeholders
Effective communication is essential for ensuring that user research findings are understood and acted upon. This involves tailoring the presentation to the audience, using clear and concise language, focusing on key findings and their implications, and providing recommendations for action. A well-structured presentation, including a clear summary of the research objectives, methodology, key findings, and recommendations, is crucial.
Visual aids, such as charts and graphs, should be used to enhance understanding. Interactive presentations or workshops can foster discussion and collaboration.
Structured Report Outlining Key Findings and Recommendations
A well-structured report should follow a clear and logical flow. It should begin with an executive summary, outlining the key findings and recommendations. This should be followed by a detailed description of the research methodology, including the participants, data collection methods, and analysis techniques. The next section should present the key findings, using visuals and data to support the claims.
Finally, the report should conclude with specific, actionable recommendations based on the findings, along with a timeline for implementation and responsible parties. For instance, a report might recommend redesigning a specific user flow based on identified usability issues, with a proposed timeline for completion and assigned team members.
Applying Findings to Improve User Experience
So, you’ve conducted your user research, analyzed the data, and now you’re staring at a mountain of insights. The real magic happens now: translating those insights into tangible improvements that genuinely enhance the user experience. This isn’t just about tweaking buttons; it’s about fundamentally improving how users interact with your product and achieve their goals.User research isn’t a one-off activity; it’s a continuous process of learning and iteration.
The insights gained should directly inform design decisions, leading to a better, more intuitive, and ultimately more successful product. This section will explore how to effectively bridge the gap between research findings and product improvements.
Translating User Research Insights into Actionable Improvements
Effective translation of user research insights requires a systematic approach. Begin by prioritizing findings based on their impact and feasibility. Focus on the most significant pain points identified and explore solutions that are both realistic to implement and align with your overall product strategy. For example, if research reveals users struggle to find a specific feature, consider redesigning the navigation or improving search functionality.
Creating user stories based on research findings helps to focus development efforts and ensures that improvements are directly addressing user needs. These stories should be clear, concise, and easily understood by the development team. For instance, “As a new user, I want to easily find the login button so I can access the app quickly.”
Case Studies of Successful Product Improvements Based on User Research
Consider the redesign of the Mailchimp email marketing platform. Extensive user research revealed that many users found the interface overwhelming and difficult to navigate. Based on these findings, Mailchimp simplified its interface, improved its onboarding process, and introduced more intuitive features. The result? Increased user satisfaction and improved user engagement.
Similarly, the redesign of the Airbnb website, driven by user research, focused on streamlining the booking process and improving search functionality, leading to significant increases in bookings and user retention. These examples demonstrate the power of user-centric design, where research directly shapes product development.
Best Practices for Iterating on Product Design Based on User Feedback
Iterative design is key. Don’t expect to solve all user experience problems in one go. Instead, implement changes in small, manageable iterations. This allows for continuous testing and refinement based on real-world user feedback. A/B testing is an invaluable tool for comparing different design iterations and measuring their impact on key metrics like conversion rates and user engagement.
Regular user feedback sessions, including usability testing and surveys, are crucial for identifying areas for improvement and validating design changes. This iterative approach ensures that the product evolves in response to actual user behavior and preferences.
The Importance of Continuous User Research for Ongoing Product Development
Continuous user research is not merely a best practice; it’s a necessity for long-term product success. The user landscape is constantly evolving, with new technologies, changing user behaviors, and emerging competitor products. Regularly collecting user feedback and conducting ongoing research helps to ensure that your product remains relevant, engaging, and competitive. This continuous feedback loop allows for proactive adaptation to changing user needs and market trends, ultimately leading to a more robust and sustainable product.
Ignoring user feedback can lead to a product that becomes outdated and irrelevant, losing market share and user loyalty.
User Interface Mockup Incorporating User Research Feedback
Let’s imagine a hypothetical e-commerce website where user research revealed that the product filtering system was confusing and inefficient. Users struggled to find specific products based on their desired criteria. The original design featured a complex filter sidebar with numerous options and unclear labels.The revised design simplifies the filtering process. The sidebar is replaced with a more intuitive dropdown menu, clearly labeled with categories like “Price,” “Brand,” “Color,” and “Size.” Each category has clear filter options.
For example, under “Price,” users can select a price range directly with slider controls. Additionally, a visual representation of filter choices is provided to enhance understanding and confirmation. This allows users to easily select and deselect filter options, and a persistent display of applied filters ensures transparency. The change ensures a smoother and more efficient product discovery experience.
This simplified approach addresses the user’s need for a more streamlined and intuitive filtering system, making it easier for them to find the products they are looking for.
Measuring the Impact of User Research

Source: notion.so
So, you’ve conducted user research – fantastic! But how do you show its value to stakeholders who might only see it as an added expense? The key is demonstrating a clear return on investment (ROI) and quantifying the positive impact on your product or service. This means moving beyond qualitative findings and embracing measurable metrics that illustrate the direct correlation between user research and business success.
Measuring the effectiveness of user research requires a multifaceted approach. It’s not just about ticking boxes; it’s about demonstrating a tangible link between research insights and improved business outcomes. This involves careful planning, the selection of appropriate KPIs, and a clear communication strategy to present your findings effectively.
Methods for Tracking and Measuring the Effectiveness of User Research Initiatives
Tracking the effectiveness of user research requires a proactive approach starting from the research design phase. We need to define specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for each research project. For example, if the goal is to improve website navigation, we might track metrics like task completion rate, bounce rate, and time on task before and after implementing design changes based on research findings.
Regular monitoring of these metrics throughout the project allows for ongoing evaluation and adjustment. A well-structured research report should explicitly state the expected impact of the research and detail how the metrics will be measured and tracked. Post-implementation analysis comparing pre- and post-research data is crucial for demonstrating the impact.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) Demonstrating the Value of User Research
Several KPIs can effectively demonstrate the value of user research. These metrics should be chosen based on the specific research goals and business objectives. For instance:
- Conversion Rate: A higher conversion rate (e.g., from website visitors to paying customers) directly reflects improved user experience based on research insights. An increase of 5% in conversion rate following the implementation of research-driven design changes is a strong indicator of success.
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT): Measuring customer satisfaction through surveys or feedback forms provides direct evidence of the positive impact of user-focused design improvements. A 10% increase in CSAT scores after implementing research-driven changes demonstrates a tangible improvement in user experience.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): NPS measures customer loyalty and willingness to recommend a product or service. A rise in NPS following research-driven changes signifies increased customer satisfaction and advocacy.
- Task Completion Rate: This metric measures the percentage of users successfully completing a specific task on a website or app. A significant increase in task completion rate demonstrates improved usability and efficiency.
- Reduced Support Tickets: User research can identify pain points and usability issues, leading to fewer support tickets. A 20% decrease in support tickets after implementing research-driven changes highlights improved product usability and reduced user frustration.
Strategies for Demonstrating the Return on Investment (ROI) of User Research Efforts
Demonstrating ROI requires translating qualitative findings into quantitative data. This involves connecting research insights to measurable business outcomes. For example, if user research identified a specific pain point that was costing the company $X in lost sales per year, and the research-driven solution reduced that loss by Y%, the cost savings can be clearly quantified. This calculation, presented in financial terms, makes the value of the research easily understandable to stakeholders.
Furthermore, comparing the cost of conducting the research to the financial gains achieved due to the implemented changes provides a clear ROI calculation. This can be presented as a simple ratio or percentage.
Presentation Showcasing the Impact of User Research on a Specific Product or Service
Imagine a scenario where user research revealed that the checkout process on an e-commerce website was confusing and leading to high cart abandonment rates. A presentation could start by showing the initial cart abandonment rate (e.g., 40%). Then, it would detail the user research methodology, highlighting key findings like specific steps in the checkout process that users found problematic.
Next, it would showcase the redesigned checkout process based on research recommendations. Finally, the presentation would display the post-implementation cart abandonment rate (e.g., 25%), clearly demonstrating a 15% reduction and a corresponding increase in revenue. Visual aids like charts and graphs would effectively communicate the data and highlight the impact of the user research.
Visual Representation of User Research Improvements Affecting Key Metrics
Before User Research Improvements:* Cart Abandonment Rate: 40%
Customer Satisfaction (CSAT)
60%
Net Promoter Score (NPS)
20After User Research Improvements:* Cart Abandonment Rate: 25% (15% reduction)
Customer Satisfaction (CSAT)
75% (15% increase)
Net Promoter Score (NPS)
40 (20% increase)
Ultimate Conclusion
Ultimately, improving our user research sprig isn’t just about collecting more data; it’s about making smarter decisions based on that data. By implementing the strategies and techniques discussed here, you can transform your user research process into a powerful engine for product innovation and user satisfaction. Remember, the key is continuous improvement and a genuine commitment to understanding your users.
So, go forth and create truly amazing user experiences!
Answers to Common Questions
What is a “user research sprig”?
It’s a metaphor representing a small, but impactful, improvement to your existing user research process. It’s about focusing on incremental changes that lead to significant overall improvements.
How much time should I dedicate to user research?
It depends on your project and resources, but continuous, iterative research is key. Even short, focused studies can provide valuable insights.
What if my users are difficult to reach?
Explore different recruitment strategies, consider online methods, and prioritize reaching your most valuable user segments first.
How do I know if my user research is effective?
Track key performance indicators (KPIs) related to user satisfaction, product improvements, and business outcomes. Did your research lead to tangible improvements?





