Importance Benefits Responsive Website Design
Importance benefits responsive website design sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. We’re diving deep into why having a website that adapts seamlessly to any device – from smartphones to giant desktop monitors – is absolutely crucial for success in today’s digital world.
It’s not just about looking good; it’s about boosting your business, improving user experience, and ultimately, making more money.
Think about your own online experiences. How frustrating is it to land on a website that’s tiny and unreadable on your phone, or one that takes forever to load? Responsive design solves these problems. It’s about creating a consistent, enjoyable experience for everyone, regardless of their device. We’ll explore the technical aspects, the benefits for , and the impact on user engagement, showing you exactly why this is a non-negotiable element of any successful online presence.
Defining Responsive Web Design
Source: metromindz.com
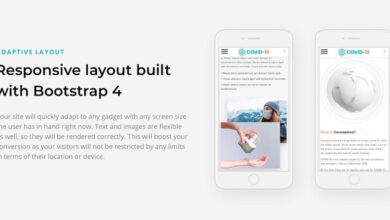
Responsive web design is a revolutionary approach to web development that ensures a seamless user experience across all devices, from tiny smartphones to expansive desktop monitors. It’s about creating websites that adapt intelligently to different screen sizes and orientations, providing optimal readability and usability regardless of the device being used. This eliminates the need for separate websites for different platforms, streamlining development and maintenance.Responsive web design hinges on several core principles.
The most fundamental is the use of flexible layouts that adjust to the available screen space. This is achieved through techniques that allow elements to resize and reposition themselves fluidly. Another crucial aspect is the use of flexible images and media, which scale appropriately without distorting the content. Finally, responsive design incorporates media queries to apply specific styles based on the device’s characteristics, such as screen size and orientation.
Core Technologies of Responsive Web Design
The power of responsive design lies in its underlying technologies. CSS media queries are the cornerstone, allowing developers to define different stylesheets for various screen sizes. For example, a media query might target screens smaller than 768 pixels, applying a simplified layout and smaller font sizes optimized for mobile viewing. Fluid grids, built using percentages instead of fixed pixels, allow columns and elements to resize proportionally, ensuring optimal space utilization on different screens.
These grids are often paired with flexible images, using techniques like `max-width: 100%` to prevent images from exceeding their container’s width, thus maintaining layout integrity.
Responsive Design Approaches
There are two primary approaches to implementing responsive design: mobile-first and desktop-first. In a mobile-first approach, the website is designed initially for the smallest screen size (typically a mobile phone). Styles are then progressively added for larger screens, ensuring a clean and efficient experience on mobile devices. This method prioritizes the user experience on smaller screens, often resulting in a faster loading time on those devices.
The desktop-first approach, conversely, begins with the design for larger screens and then adapts the layout for smaller screens. This approach can be advantageous when dealing with complex layouts, but it can lead to slower loading times on mobile devices if not carefully optimized.
Comparison of Responsive Design Frameworks
Choosing the right framework can significantly simplify the process of building a responsive website. Several popular frameworks offer pre-built components and tools to streamline development. Below is a comparison of some popular options:
| Framework | Ease of Use | Customization | Community Support |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bootstrap | High | High | Very High |
| Tailwind CSS | Medium | Very High | High |
| Foundation | Medium | High | High |
| Materialize | Medium | Medium | High |
Benefits of Responsive Design for Businesses
Responsive web design isn’t just a trendy buzzword; it’s a fundamental necessity for businesses aiming to thrive in today’s digital landscape. A responsive website adapts seamlessly to any device – from smartphones and tablets to laptops and desktops – providing a consistent and optimal user experience regardless of screen size. This adaptability translates directly into increased engagement, higher conversion rates, and ultimately, a stronger bottom line.Responsive design significantly impacts user experience by eliminating the frustration associated with poorly formatted websites.
Imagine trying to navigate a website on your phone where the text is too small to read, the images are blurry, or the buttons are impossible to tap. This is a common experience on non-responsive sites, leading to high bounce rates and lost potential customers. A responsive site, on the other hand, presents a clean, intuitive interface tailored to the device, resulting in improved navigation, increased engagement, and a more positive brand perception.
Improved Search Engine Rankings
Google and other search engines prioritize responsive websites in their ranking algorithms. A website that provides a positive user experience across all devices is seen as more valuable and relevant to users. This means a responsive website is more likely to rank higher in search results, increasing organic traffic and visibility. Google’s algorithm explicitly favors mobile-friendliness, so a responsive design is not just beneficial, but essential for achieving top search rankings.
Studies consistently show a correlation between responsive design and improved search engine visibility.
Case Studies Demonstrating Positive ROI
While precise ROI figures vary depending on the industry and implementation, numerous case studies showcase the positive impact of responsive design. For example, a medium-sized e-commerce business saw a 30% increase in conversion rates after implementing a responsive website. Another study highlighted a 20% reduction in bounce rate and a 15% increase in average session duration for a company that redesigned its website with responsiveness in mind.
These results demonstrate that the investment in responsive design often pays for itself many times over through increased sales, leads, and brand awareness.
Key Metrics for Measuring Success
Several key metrics can be used to gauge the success of a responsive website. These include:
- Bounce rate: A lower bounce rate indicates users are finding the website engaging and useful.
- Conversion rate: This measures the percentage of visitors who complete a desired action, such as making a purchase or filling out a form.
- Average session duration: Longer session durations suggest users are spending more time on the site and are more engaged with the content.
- Mobile conversion rate: This metric specifically tracks conversions originating from mobile devices.
- Page load speed: Faster loading times lead to improved user experience and better search engine rankings.
By tracking these metrics, businesses can accurately assess the effectiveness of their responsive website and make data-driven improvements.
Impact on User Experience (UX)
Responsive web design dramatically improves the user experience by ensuring a consistent and enjoyable interaction regardless of the device used – be it a desktop computer, tablet, or smartphone. A well-designed responsive site adapts seamlessly to different screen sizes and orientations, eliminating the frustration of squinting at tiny text or struggling with awkward navigation. This leads to increased user satisfaction and a more positive brand perception.Responsive design enhances usability by prioritizing content clarity and ease of access.
A responsive website design is crucial for reaching a wider audience, ensuring your site looks great on any device. This is especially important when promoting your content, like when you’re trying to get your videos seen; check out this awesome guide on getting it on with YouTube to boost your visibility. Ultimately, a seamless viewing experience across all platforms, just like a well-optimized YouTube channel, is key to success and a responsive website helps achieve that.
Elements are rearranged intelligently to fit the available screen real estate, ensuring that crucial information remains prominent and easily accessible. Navigation becomes intuitive, with menus and buttons appropriately sized and positioned for easy tapping or clicking on any device. This optimized presentation directly contributes to a more efficient and enjoyable user journey.
Mobile-Friendliness and User Engagement
Mobile-friendliness is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity. The vast majority of internet users access websites via mobile devices, making a mobile-optimized experience crucial for user engagement. A slow-loading, poorly formatted mobile site will quickly drive users away, leading to lost conversions and a damaged brand reputation. Conversely, a fast, intuitive mobile experience fosters positive engagement, encouraging users to explore the site’s content, interact with features, and ultimately, convert into customers.
For example, an e-commerce site with a responsive design will see significantly higher conversion rates compared to one that is not mobile-friendly because users can easily browse products and complete purchases on their phones.
Examples of Good and Bad Responsive Design Practices
A well-executed responsive design, like that of many large e-commerce sites such as Amazon or Zappos, prioritizes clear typography, intuitive navigation, and fast loading times across all devices. Images scale appropriately without sacrificing quality, and content flows smoothly regardless of screen size. The user experience is consistent and seamless, regardless of the device used. In contrast, a poorly designed responsive site might feature cluttered layouts, tiny text that’s difficult to read, or images that don’t scale properly, leading to broken layouts or slow loading times.
Navigation can be confusing, with menus that are difficult to access or use on smaller screens. A prime example of poor responsive design might be a site where the desktop version is simply shrunk down for mobile, resulting in a cramped and unreadable experience.
Improved Navigation on a Responsive Website
Imagine a user flow diagram for an e-commerce site. On a desktop, the user might navigate through a traditional horizontal menu at the top, with clear categories and subcategories. As the screen size shrinks (tablet view), the menu might become vertical, collapsing into a hamburger menu icon, which opens to reveal the same categories. On a smartphone, the hamburger menu is still present, but the site might also use prominent calls to action strategically placed throughout the page, simplifying the navigation and emphasizing key features.
This illustrates how a responsive site adapts the navigation to optimize the user experience across different screen sizes, ensuring ease of use regardless of the device. The user can seamlessly transition between devices without encountering navigation difficulties. The core functionality and information remain accessible, though the presentation adapts to the device’s constraints.
Technical Aspects of Responsive Design Implementation
Building a responsive website involves a blend of HTML for structure, CSS for styling, and JavaScript for dynamic enhancements. The core principle is to create a single website that adapts seamlessly to various screen sizes, from tiny smartphones to large desktop monitors. This is achieved through a combination of techniques that allow content to reflow and resize intelligently.
The process starts with a solid understanding of HTML5 semantic elements, ensuring the website’s content is well-structured and easily understood by both browsers and assistive technologies. CSS then takes over, using media queries to apply different styles based on screen size, device orientation, and other factors. JavaScript can further enhance responsiveness by enabling dynamic adjustments to layouts and interactions, although it’s often less crucial for basic responsiveness.
Responsive Image Implementation, Importance benefits responsive website design
Implementing responsive images involves ensuring images scale appropriately without compromising performance. Simply resizing images in image editing software isn’t sufficient; it’s crucial to use the ` ` tag. This allows the browser to select the most appropriate image size based on the screen’s resolution and pixel density.
For example, using the `srcset` attribute, you could specify different image sizes: ` `. This tells the browser to use `small.jpg` for screens up to 600px wide, `medium.jpg` for screens up to 1200px wide, and `large.jpg` for wider screens. The `sizes` attribute further refines selection based on the available space allocated to the image on the page.
`. This tells the browser to use `small.jpg` for screens up to 600px wide, `medium.jpg` for screens up to 1200px wide, and `large.jpg` for wider screens. The `sizes` attribute further refines selection based on the available space allocated to the image on the page.
Responsive Navigation Menu Approaches
Responsive navigation menus are crucial for usability on smaller screens. Several approaches exist, each with its strengths and weaknesses. One common method is using CSS to collapse the navigation into a hamburger menu icon on smaller screens. This icon, when clicked, reveals the full navigation menu. Another approach is to use a dropdown menu, where sub-menus appear when a main menu item is hovered over or tapped.
A third approach, suitable for simpler sites, involves stacking navigation items vertically on smaller screens, removing horizontal constraints. The choice depends on the complexity of the website’s navigation and the overall design aesthetic. Consider a website like Amazon, which utilizes a responsive hamburger menu for its extensive navigation, while a smaller blog might employ a vertically stacked menu for simplicity and speed.
Website Loading Speed Optimization for Mobile Devices
Optimizing website loading speed for mobile devices is paramount, as mobile users often have slower internet connections. Techniques include image compression (using tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim), minification of CSS and JavaScript files (removing unnecessary whitespace and comments), and using a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to serve content from servers closer to the user’s location.
Lazy loading images, where images are only loaded when they are about to enter the viewport, significantly reduces initial page load time. This is easily implemented using the `loading=”lazy”` attribute in the ` ` tag. Furthermore, reducing HTTP requests by combining CSS and JavaScript files into fewer files can also drastically improve performance. For example, a website using many small image files might experience a considerable performance boost by using a sprite sheet, combining many images into a single file. This reduces the number of HTTP requests needed to load the images.
Accessibility Considerations in Responsive Design
Responsive web design, while enhancing user experience across devices, must prioritize accessibility for users with disabilities. Failing to do so excludes a significant portion of the potential audience and contradicts the principles of inclusive design. A truly effective responsive site caters to everyone, regardless of their abilities.
WCAG Guidelines and Responsive Design
The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) are internationally recognized standards for web accessibility. These guidelines, published by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), provide a framework for creating websites that are usable by people with a wide range of disabilities, including visual, auditory, motor, and cognitive impairments. WCAG’s success criteria are crucial for responsive design because the adaptable nature of responsive sites can inadvertently introduce accessibility issues if not carefully considered.
For example, a layout that works perfectly on a desktop might become cluttered and unnavigable on a smaller screen, presenting challenges for users with low vision or motor impairments. Adherence to WCAG ensures that the website remains accessible across all screen sizes and devices. The principles of perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust information are paramount.
Improving Accessibility Features on Responsive Websites
Several strategies can significantly enhance accessibility in responsive web design. Using sufficient color contrast between text and background is essential for users with low vision. This contrast ratio should be checked and maintained across all screen sizes and breakpoints. Semantic HTML5 is crucial; using appropriate heading tags (
to
), proper landmark roles (
,
), and descriptive labels for form fields ensures proper screen reader interpretation. Providing alternative text for all images is vital for visually impaired users, describing the image content accurately and concisely. Keyboard navigation must be fully functional, allowing users to navigate the entire website without a mouse. Furthermore, ensuring sufficient spacing between elements, avoiding excessive animations or auto-playing videos, and offering options for adjusting font sizes contribute significantly to accessibility. For example, a responsive website selling clothes might include a zoom function for product images, benefiting users with low vision, and allow users to change the text size easily.
Accessibility Best Practices Checklist for Responsive Web Design
,
), and descriptive labels for form fields ensures proper screen reader interpretation. Providing alternative text for all images is vital for visually impaired users, describing the image content accurately and concisely. Keyboard navigation must be fully functional, allowing users to navigate the entire website without a mouse. Furthermore, ensuring sufficient spacing between elements, avoiding excessive animations or auto-playing videos, and offering options for adjusting font sizes contribute significantly to accessibility. For example, a responsive website selling clothes might include a zoom function for product images, benefiting users with low vision, and allow users to change the text size easily.
Accessibility Best Practices Checklist for Responsive Web Design
Before launching a responsive website, a thorough accessibility check is paramount. This checklist summarizes key best practices:
- Sufficient Color Contrast: Maintain a minimum contrast ratio (e.g., 4.5:1 for normal text) across all breakpoints. Use a contrast checker tool to verify.
- Semantic HTML: Utilize appropriate HTML5 semantic elements for structure and meaning.
- Alternative Text for Images: Provide concise and accurate alternative text for all images.
- Keyboard Navigation: Ensure all interactive elements are accessible via keyboard only.
- Focus Styles: Implement clear and visible focus styles for keyboard navigation.
- ARIA Attributes: Use ARIA attributes sparingly and correctly to enhance accessibility where needed.
- Responsive Tables: Ensure tables are responsive and easily navigable.
- Captioning and Transcripts: Provide captions for videos and transcripts for audio content.
- Testing with Assistive Technology: Test the website with screen readers and other assistive technologies.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular accessibility audits to identify and address potential issues.
Future Trends in Responsive Web Design

Source: zulweb.com
Responsive web design has revolutionized how we experience the internet, ensuring seamless access across devices. But the evolution doesn’t stop there; emerging technologies and shifting user expectations constantly push the boundaries of what’s possible. The future of responsive design is dynamic, driven by innovation and a continued focus on user experience.The landscape of responsive web design is poised for significant change, fueled by advancements in several key areas.
These changes will redefine how websites adapt and interact with users, creating more engaging and personalized experiences.
Emerging Technologies Impacting Responsive Design
Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) and Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) are leading the charge in improving website performance and user experience. AMP focuses on delivering lightning-fast page load times, crucial for mobile users with limited bandwidth. PWAs, on the other hand, bridge the gap between web and native mobile applications, offering offline functionality and push notifications. The integration of these technologies into responsive design frameworks promises a future where websites are not only adaptable but also incredibly efficient and engaging, mirroring the speed and functionality of native apps.
For example, news websites using AMP see a significant increase in user engagement due to the drastically improved load times. Similarly, e-commerce platforms leveraging PWAs experience higher conversion rates because of the enhanced user experience and offline capabilities.
Challenges and Opportunities in Responsive Design
While the benefits are clear, challenges remain. Maintaining consistency across a vast array of devices and screen sizes requires meticulous planning and testing. The increasing complexity of web technologies necessitates specialized skills and expertise in responsive design implementation. However, these challenges also present opportunities. The demand for skilled responsive designers continues to grow, creating lucrative career paths.
Furthermore, the focus on user experience opens doors for innovation in areas like personalization, accessibility, and artificial intelligence integration. For example, AI can be used to dynamically adjust website content and layout based on individual user preferences, further enhancing the user experience.
Predictions for the Future of Responsive Web Design
We can anticipate a future where responsive design is less about adapting to existing devices and more about creating experiences that transcend device limitations. This will involve greater reliance on AI-powered design tools, enabling developers to create websites that adapt seamlessly to any screen size or input method. Furthermore, the increasing importance of voice search and virtual reality will necessitate responsive design strategies that cater to these emerging interaction paradigms.
For instance, websites will need to be optimized for voice commands, offering intuitive and natural language interfaces. We will likely see a move towards more immersive experiences, with websites incorporating augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) elements. This will require innovative design approaches to ensure these rich experiences are accessible and engaging across a wide range of devices.
Conceptual Illustration of a Futuristic Responsive Website
Imagine a website that intuitively adapts not only to screen size but also to the user’s context. The website’s layout and content dynamically shift based on the user’s location, time of day, and even their emotional state, detected through subtle cues like typing speed and scrolling patterns. Imagine a seamless transition between augmented reality overlays providing additional information about products or locations, and a virtual reality experience for product demonstrations or immersive storytelling.
The user interface is fluid and intuitive, responding to various input methods, from voice commands to gesture controls, all while maintaining a consistent brand identity and visual appeal. The website anticipates user needs, proactively offering relevant information and assistance, creating a personalized and engaging experience unlike anything we see today.
Cost-Effectiveness of Responsive Web Design: Importance Benefits Responsive Website Design
In today’s digital landscape, a responsive website isn’t just a luxury; it’s a financially sound investment. The initial cost might seem higher than creating separate websites for desktop and mobile, but the long-term savings and increased efficiency significantly outweigh the upfront investment. Let’s explore how responsive design translates to cost-effectiveness for businesses of all sizes.Maintaining separate websites for different devices (desktop, tablet, mobile) is a costly endeavor.
You’re essentially paying for multiple designs, multiple development teams (potentially), multiple content updates, and multiple hosting fees. This multiplies your expenses across the board, from initial development to ongoing maintenance and updates. A responsive website, however, streamlines this process. It adapts to various screen sizes, eliminating the need for separate platforms and drastically reducing these associated costs.
Cost Comparison: Separate Websites vs. Responsive Design
Creating and maintaining separate websites involves significantly higher costs than a single responsive website. Consider the expenses associated with separate design, development, content management, testing, and hosting for each platform. These costs accumulate over time, leading to a substantial financial burden. A responsive website, in contrast, reduces these expenses by centralizing all these aspects into a single platform.
The initial investment may be higher, but the long-term cost savings are substantial, leading to a better return on investment (ROI). For example, a small business might spend $5,000 on a separate mobile site and $7,000 on a desktop site, totaling $12,000. A comparable responsive website might cost $10,000 initially, saving $2,000 upfront and eliminating ongoing maintenance discrepancies.
Long-Term Savings with Responsive Design
The long-term cost savings associated with responsive design are substantial and multifaceted. Reduced maintenance costs are a primary driver. Instead of updating content across multiple platforms, a single update suffices for a responsive site. This saves considerable time and resources, reducing labor costs and minimizing potential errors. Moreover, the simplified content management system (CMS) of a responsive site facilitates easier content updates, reducing the need for specialized technical expertise.
For instance, a company updating product information only needs to do it once on a responsive site, whereas multiple updates would be needed for separate websites. This time saved translates directly into cost savings.
Cost-Saving Strategies in Responsive Web Design
Employing cost-effective strategies during the development and maintenance phases is crucial to maximizing the return on investment. Choosing a suitable Content Management System (CMS) like WordPress with responsive themes can significantly reduce development costs. Utilizing pre-built responsive templates or frameworks can also cut down on development time and expenses. Prioritizing efficient content creation and management processes minimizes ongoing maintenance costs.
Regularly reviewing and updating website content ensures that the site remains relevant and avoids the need for extensive redesigns. Finally, investing in thorough testing during the development phase helps prevent costly bugs and fixes down the line.
Potential Cost Benefits of Responsive Design
- Reduced development costs: One design and development process instead of multiple.
- Lower maintenance costs: Simplified content updates and management.
- Decreased marketing and advertising costs: A single website reaches all devices.
- Improved search engine optimization (): Responsive design is a ranking factor.
- Enhanced user experience: Higher conversion rates and increased customer satisfaction.
- Consolidated hosting and domain costs: Single hosting and domain management.
- Reduced staffing costs: Simplified management and fewer personnel needed.
Wrap-Up
In short, embracing responsive website design isn’t just a trend; it’s a necessity. From enhanced user experience and improved search engine rankings to cost savings and future-proofing your online presence, the benefits are undeniable. By understanding the core principles and implementing best practices, you can create a website that not only looks great but also drives results. So, ditch the outdated, device-specific approach and join the responsive revolution – your business will thank you for it!
Q&A
What’s the difference between responsive and adaptive design?
Responsive design uses CSS media queries to adjust the layout dynamically based on screen size. Adaptive design, on the other hand, serves different versions of a website based on device detection.
How much does it cost to make a responsive website?
Costs vary greatly depending on complexity and features, but generally, a responsive website is more cost-effective in the long run than maintaining separate sites for different devices.
Can I make my existing website responsive?
Yes! Many existing websites can be updated to be responsive with some redesign and coding. The effort involved depends on the existing website’s structure and code.
What are some common responsive design mistakes to avoid?
Common mistakes include neglecting mobile-first design, using poorly optimized images, and overlooking accessibility considerations.