Google Analytics 4 Takeover What You Need to Know
Google analytics 4 takeover what you need to know – Google Analytics 4 takeover: what you need to know! The Universal Analytics (UA) era is ending, and Google Analytics 4 (GA4) is taking the reins. This isn’t just a minor update; it’s a complete overhaul of how we track website data. This post will break down the key differences between UA and GA4, guide you through the migration process, and equip you with the knowledge to leverage GA4’s powerful features to boost your website’s performance.
Get ready to navigate the exciting, yet sometimes daunting, world of GA4!
We’ll cover everything from understanding the new interface and mastering its key metrics to implementing effective tracking and drawing actionable insights from your data. Think of this as your ultimate survival guide to the GA4 revolution. Whether you’re a seasoned analytics pro or just starting out, this comprehensive guide will help you confidently navigate the transition and harness the full potential of GA4.
Understanding the GA4 Transition
Source: windsor.ai
The shift from Universal Analytics (UA) to Google Analytics 4 (GA4) represents a significant change in how businesses track and analyze website traffic. This transition isn’t just a minor update; it’s a fundamental shift in the underlying architecture and data processing, necessitating a proactive approach from all businesses reliant on Google Analytics for data-driven decision-making. Understanding the differences, the timeline, and the migration process is crucial for a smooth transition and avoiding data loss.
Key Differences Between UA and GA4
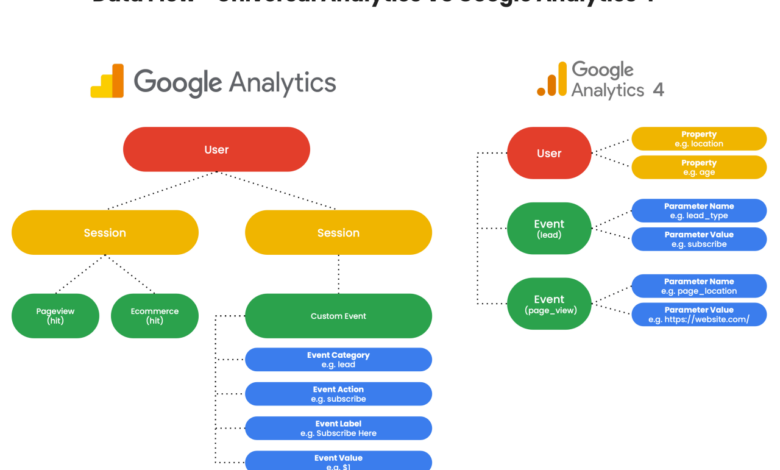
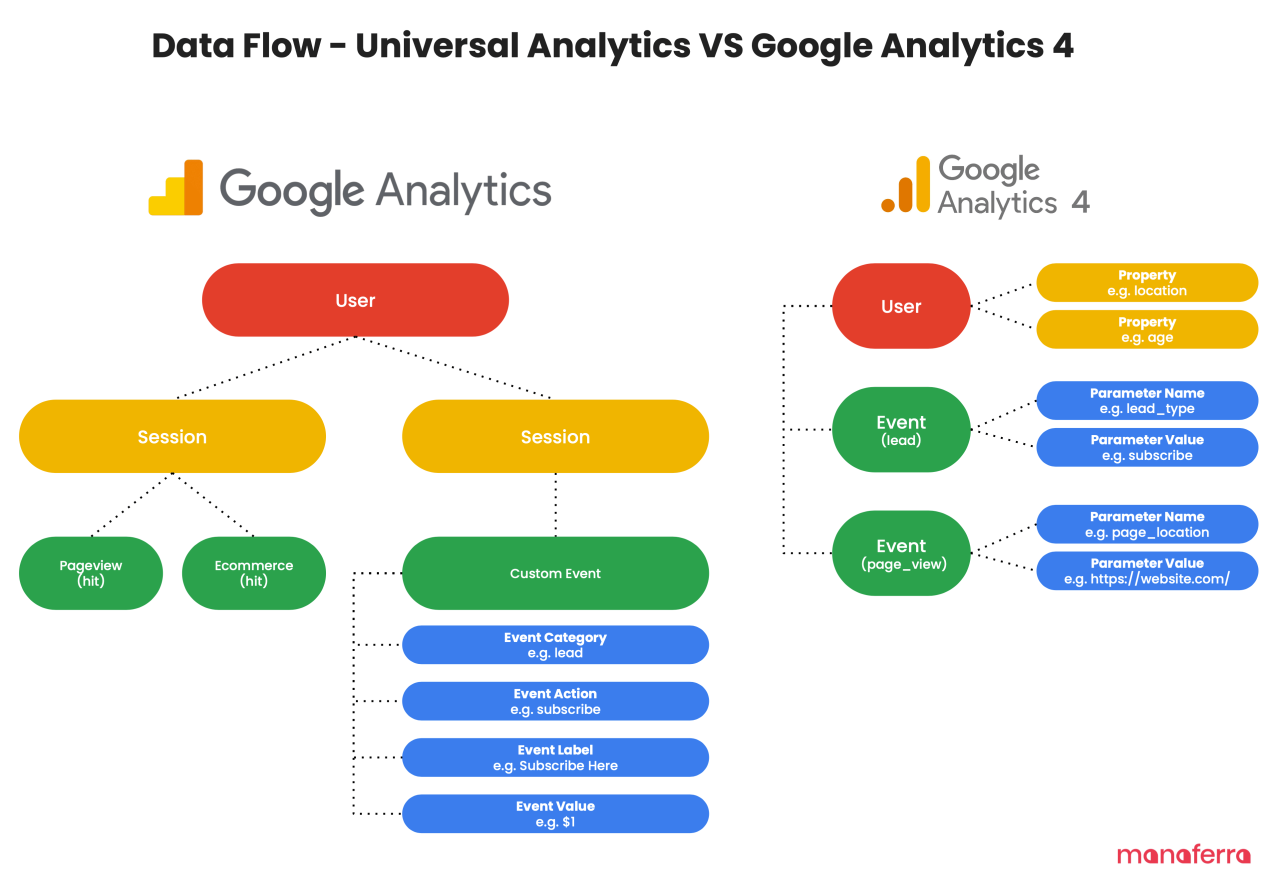
Universal Analytics (UA) and Google Analytics 4 (GA4) differ significantly in their data models, reporting features, and overall approach to website analytics. UA, a more traditional model, relies heavily on session-based data, focusing on pageviews and bounce rates. GA4, however, adopts a more event-based model, providing a more holistic view of user behavior across platforms. This allows for a more comprehensive understanding of the customer journey.
This shift necessitates a change in how businesses approach data collection and analysis.
The UA Sunset and its Implications
Universal Analytics officially sunsetted on July 1, 2023. This means that UA properties stopped processing new hits. Businesses that continued to rely solely on UA after this date experienced a complete loss of new data. This has significant implications, as historical data from UA is no longer updated and new data collection is impossible. Companies that failed to migrate to GA4 before the deadline are now unable to track current website performance through UA.
This data loss can severely hinder marketing strategies and decision-making processes, highlighting the critical importance of timely migration. For example, a company relying solely on UA to track campaign performance would be unable to analyze the success of ongoing campaigns after the sunset date.
Step-by-Step Guide for Migrating from UA to GA4
Migrating from UA to GA4 involves several key steps. It’s not simply a matter of switching a setting; it requires careful planning and execution. Here’s a step-by-step guide to ensure a smooth transition:
- Create a GA4 Property: Within your existing UA property, you can create a new GA4 property. This is the foundational step. Google provides clear instructions within the platform to guide you through this process.
- Configure Data Streams: Connect your website and apps to your GA4 property. This ensures data is properly collected and categorized.
- Set up Event Tracking: Define and track key events relevant to your business goals. This is crucial for understanding user interactions in the event-based GA4 model.
- Compare Data: Run parallel reports in both UA and GA4 to compare data and identify discrepancies. This helps in adjusting configurations and ensuring data accuracy.
- Implement Enhanced Measurement: Utilize GA4’s enhanced measurement features to automatically collect data on key interactions, simplifying the setup process.
- Analyze and Adjust: Continuously monitor your GA4 data and make adjustments as needed to optimize data collection and reporting.
Comparison of Key Features
The following table highlights key differences between UA and GA4:
| Feature | Universal Analytics (UA) | Google Analytics 4 (GA4) | Key Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Model | Session-based | Event-based | GA4 offers a more granular view of user behavior across multiple platforms. |
| Cross-Platform Tracking | Limited | Robust | GA4 excels at tracking user journeys across websites and apps. |
| Real-time Reporting | Available, but less comprehensive | More comprehensive and detailed | GA4 provides more immediate insights into user activity. |
| Machine Learning | Limited | Extensive | GA4 leverages machine learning for predictive analytics and enhanced insights. |
Navigating the GA4 Interface
GA4 represents a significant shift from Universal Analytics, and understanding its interface is crucial for effective data analysis. This walkthrough will highlight key areas and reports to help you become comfortable navigating the platform and extracting valuable insights. The interface, while initially appearing complex, is logically structured once you understand the core reporting principles.The GA4 interface is organized around key areas: Real-time reporting provides an immediate view of current website activity.
Reports offer detailed breakdowns of user behavior, and the Explore section allows for custom analysis. Finally, the Administration section handles property settings and user management.
GA4 Reporting Structure
Imagine a pyramid. At the apex sits the “Overview” report, providing a high-level summary of key metrics like users, sessions, and engagement. The next level branches into acquisition, engagement, monetization, and retention reports, each focusing on a specific area of user interaction. These reports then further subdivide into more granular reports providing detailed metrics. For instance, the Acquisition report might break down traffic sources into organic search, paid campaigns, and social media.
Engagement delves into page views, event tracking, and user engagement time. Monetization focuses on revenue and conversion metrics, while Retention tracks user loyalty and returning visits. This hierarchical structure allows for a progressive drilling down from broad overviews to specific detailed analysis.
Custom Reports and Dashboards
GA4 empowers users to create custom reports and dashboards tailored to specific needs. This is invaluable for focusing on key performance indicators (KPIs) relevant to business goals. To create a custom report, you start by selecting a report type (e.g., freeform, funnel, path exploration) and then defining the dimensions and metrics you want to analyze. Dimensions provide context (e.g., country, device), while metrics quantify the data (e.g., sessions, bounce rate, revenue).
You can then save these reports and incorporate them into custom dashboards for easy access and monitoring. For example, a marketing team might create a custom dashboard displaying key metrics for their ongoing campaigns, allowing them to quickly assess performance and make data-driven adjustments. A custom report might focus solely on conversion rates from a specific marketing channel.
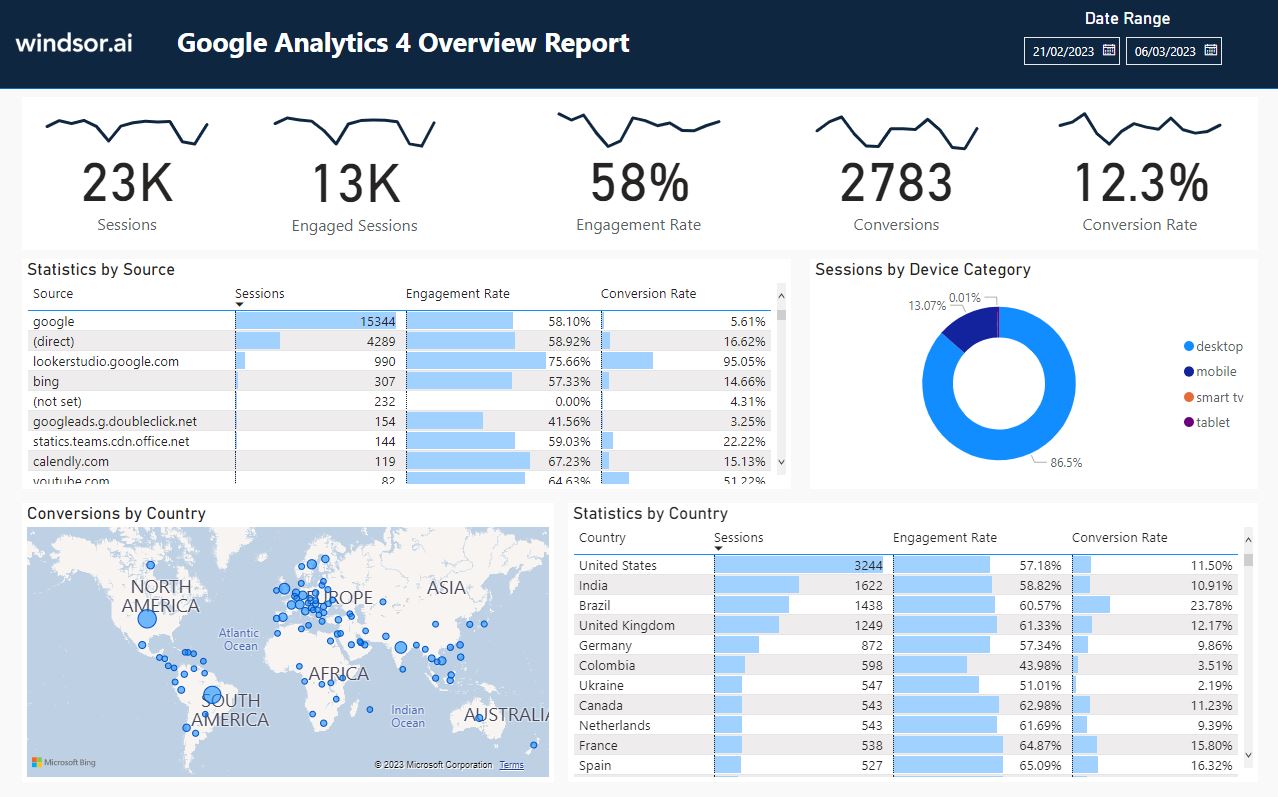
Essential GA4 Reports for Website Performance Monitoring
Understanding which reports to prioritize is crucial for efficient analysis. Here’s a list of essential reports for monitoring website performance:
- Overview Report: Provides a high-level summary of key website metrics. This is your starting point for any analysis.
- Acquisition Report: Identifies the sources driving traffic to your website (e.g., organic search, social media, paid campaigns).
- Engagement Report: Analyzes user behavior on your website, including page views, event tracking, and engagement metrics.
- Monetization Report: Tracks revenue and conversion data, crucial for e-commerce websites.
- Retention Report: Measures user loyalty and returning visits, indicating the effectiveness of retention strategies.
- Real-time Report: Provides a live view of current website activity.
These reports, used in conjunction with custom reports and dashboards, provide a comprehensive understanding of website performance and user behavior, enabling data-driven decision-making.
Key GA4 Metrics and Dimensions

Source: alias2k.com
Understanding the key metrics and dimensions in Google Analytics 4 (GA4) is crucial for effectively measuring your website or app’s performance and achieving your business goals. GA4 represents a significant shift from Universal Analytics (UA), demanding a reassessment of how you track and interpret your data. This section will highlight the most important metrics, compare them to UA counterparts, and explain the power of event-based tracking in GA4.GA4’s event-based data model is a fundamental difference from UA’s pageview-centric approach.
This means almost all interactions on your site or app are recorded as events, providing a far richer and more granular understanding of user behavior. This allows for deeper insights into user engagement and conversion paths.
Important Metrics for Different Business Goals
Choosing the right metrics depends entirely on your business objectives. For example, an e-commerce site will prioritize different metrics than a blog. However, some metrics are universally valuable.
- Engagement: Engagement metrics reveal how users interact with your content. Key indicators include engaged sessions (sessions lasting longer than 10 seconds or with two or more events), engagement rate (percentage of sessions that are engaged), and average engagement time. These metrics provide insights into user interest and the effectiveness of your content.
- Conversions: Conversions represent valuable actions users take on your site or app, such as purchases, sign-ups, or form submissions. Defining and tracking these conversions is essential for measuring marketing ROI. GA4 allows for flexible conversion definitions, including both event-based and revenue-based conversions.
- Monetization: For businesses generating revenue, metrics like revenue, average revenue per user (ARPU), and conversion rate are critical. GA4’s enhanced ecommerce tracking provides detailed information on revenue and transaction data.
- Acquisition: Understanding how users discover your website or app is vital. Metrics like user acquisition, session source/medium, and acquisition cost help determine the effectiveness of your marketing channels.
Comparison of Key Metrics in UA and GA4
The transition from UA to GA4 necessitates understanding the differences in key metrics. While some metrics have direct equivalents, others are fundamentally different due to the shift to an event-based model.
| Metric | UA | GA4 | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sessions | Pageviews and sessions | Sessions and engaged sessions | GA4 emphasizes engaged sessions, providing a more accurate representation of meaningful user interaction. |
| Bounce Rate | Percentage of single-page sessions | Engagement rate and average engagement time | GA4 replaces bounce rate with engagement metrics, offering a more nuanced view of user behavior. |
| Conversions | Goals | Events configured as conversions | GA4 provides more flexibility in defining and tracking conversions. |
| Revenue | E-commerce tracking | Enhanced ecommerce tracking | GA4’s enhanced ecommerce tracking offers more granular data on revenue and transactions. |
The Significance of Event-based Tracking in GA4
GA4’s event-based data model is its defining characteristic. Unlike UA, which primarily relied on pageviews, GA4 treats almost all user interactions as events. This allows for a more comprehensive understanding of user behavior, enabling businesses to track a wider range of actions and interactions. For example, a simple button click, a video play, or a form submission are all captured as individual events, providing detailed insights into user engagement with specific elements on your website or app.
This granularity enables more precise analysis and informed decision-making.
Using Dimensions to Segment Data in GA4
Dimensions provide context to your metrics. They allow you to segment your data and gain deeper insights into user behavior. For example, you can segment your conversion data by source/medium to understand which marketing channels are driving the most conversions.
- Segmenting by User Demographics: GA4 provides access to user demographics like age and location. Segmenting your data by these dimensions can reveal which demographics are most engaged with your content.
- Segmenting by Event Properties: Each event in GA4 can have associated properties. These properties provide further context to the event. For example, if you’re tracking a “purchase” event, properties might include product ID, price, and quantity. Segmenting your conversion data by these properties can help identify your best-selling products.
- Segmenting by User Acquisition Channel: Analyzing conversion rates by acquisition channel helps you understand the effectiveness of your marketing efforts. You can identify which channels are driving the most valuable users.
Implementing GA4 Tracking
Source: manaferra.com
Getting your GA4 property correctly configured for tracking is crucial for accurate data analysis and informed decision-making. This involves setting up event tracking for various user interactions, configuring e-commerce tracking for sales data, and integrating GA4 with other marketing platforms to gain a holistic view of your marketing performance. Let’s delve into the specifics.
Event Tracking Setup
Proper event tracking allows you to understand user behavior on your website beyond simple pageviews. By tracking button clicks, form submissions, and other interactions, you gain valuable insights into user engagement and conversion paths. This involves defining events, parameters, and setting up triggers within your GA4 configuration. For example, a button click event might include parameters such as the button’s location on the page and the associated action.
A form submission might include parameters like the form name and the data submitted.
E-commerce Tracking Configuration
Setting up e-commerce tracking in GA4 provides essential data on your online sales performance. This involves configuring enhanced e-commerce settings within your GA4 property. You’ll need to define parameters for products, transactions, and revenue. GA4 uses events like `begin_checkout`, `add_to_cart`, `purchase`, and others to capture the entire customer journey. This detailed information allows you to track key metrics such as conversion rates, average order value, and revenue generated from different marketing channels.
Proper configuration requires careful mapping of your e-commerce platform’s data to GA4’s event schema.
GA4 Integration with Other Marketing Tools
Integrating GA4 with other marketing tools like Google Ads, CRM systems, and marketing automation platforms allows for a unified view of your marketing performance. This integration facilitates advanced analysis, enabling you to connect online activity to offline conversions and attribute revenue to specific marketing campaigns more accurately. For example, integrating with Google Ads allows for importing conversion data, enabling more effective ad targeting and optimization.
Connecting with a CRM system provides a complete picture of the customer lifecycle, from initial website interaction to post-purchase engagement. The integration methods vary depending on the specific tool, often involving APIs or dedicated connectors.
GA4 Data Collection Checklist
Before relying on your GA4 data, ensure its accuracy by verifying the following:
A comprehensive checklist is essential for ensuring accurate data collection. Here’s a list of crucial steps to confirm your GA4 setup is functioning correctly:
- Verify Property Setup: Double-check that your GA4 property is correctly configured and linked to your website.
- Test Event Tracking: Use the GA4 Realtime report to verify that events are being recorded accurately. Trigger various interactions on your website and check for corresponding events in the Realtime report.
- Review E-commerce Data: If you have e-commerce tracking enabled, carefully review your transaction data to ensure accuracy. Compare the data with your e-commerce platform’s reporting.
- Check Data Consistency: Compare GA4 data with your previous analytics platform (e.g., Universal Analytics) to identify any significant discrepancies. This helps pinpoint potential configuration issues.
- Regular Data Audits: Perform regular audits of your GA4 data to ensure continued accuracy and identify any emerging issues.
Analyzing GA4 Data for Insights
Unlocking the power of Google Analytics 4 (GA4) goes beyond simply collecting data; it’s about transforming raw numbers into actionable insights that drive website improvements. This section explores effective methods for analyzing GA4 data to understand user behavior, segment audiences, and ultimately boost conversion rates. We’ll delve into practical techniques and illustrate how to derive meaningful conclusions from your GA4 reports.
Identifying User Engagement Patterns
Understanding how users interact with your website is crucial. GA4 provides various tools to analyze engagement patterns. By examining metrics like session duration, pages per session, bounce rate, and event tracking data, you can identify areas of high and low engagement. For example, a high bounce rate on a specific landing page suggests potential issues with its content or design, prompting a review of the page’s effectiveness.
Conversely, long session durations on particular product pages could indicate strong user interest and potential for improved conversions. Analyzing engagement across different devices and user demographics can further refine your understanding.
Segmenting Audiences Based on User Behavior
GA4’s robust segmentation capabilities allow you to create detailed user profiles based on their actions. You can segment audiences based on demographics (age, location), technology (device, browser), acquisition source (organic search, paid advertising), and behavior (engagement, conversions). For instance, you might segment users who have added items to their cart but didn’t complete the purchase. This segment allows for targeted remarketing campaigns focusing on abandoned carts, potentially employing email reminders or personalized offers to encourage completion.
Another example could be segmenting users based on specific events, such as watching a video or downloading a resource, to tailor future content and offerings.
Utilizing GA4 Data to Improve Website Conversion Rates
GA4 data directly informs strategies to improve conversion rates. By analyzing the user journey from initial engagement to conversion, you can identify bottlenecks and areas for optimization. For example, if the conversion rate is low for users arriving from a particular marketing campaign, you can adjust the campaign’s targeting or messaging. Analyzing the performance of different landing pages can highlight which ones are most effective at converting visitors into customers.
This analysis can be combined with A/B testing to continuously improve conversion funnels.
Examples of Actionable Insights from GA4 Data
Consider a hypothetical e-commerce website. GA4 reveals a high bounce rate on the product category page for “women’s shoes.” This suggests that users find it difficult to navigate or locate the specific shoes they’re looking for. Actionable insights might include improving the site search functionality, adding better filtering options, or redesigning the category page for improved usability. Alternatively, if GA4 data shows that users who engage with product videos have a higher conversion rate, this suggests that investing in more high-quality product videos could significantly increase sales.
Another example could be identifying a specific demographic segment (e.g., 25-35 year-old women) with a high conversion rate from a particular social media campaign, suggesting an opportunity to refine targeting and increase investment in that channel.
GA4 Reporting and Visualization
GA4 offers a powerful suite of reporting and visualization tools to help you understand your website’s performance. Moving beyond the familiar interface of Universal Analytics, GA4 emphasizes exploration and the creation of custom reports tailored to your specific business needs. Mastering these tools is crucial for extracting actionable insights and effectively communicating your findings to stakeholders.
Effective data visualization is key to making your GA4 data understandable and impactful. By leveraging GA4’s built-in features, you can transform raw data into compelling narratives that highlight key trends and areas for improvement. This involves selecting the right chart types for different data points, ensuring clear labeling, and presenting information in a logical and easy-to-follow manner.
Creating Effective Visualizations, Google analytics 4 takeover what you need to know
GA4 provides various visualization options, including charts, tables, and even free-form explorations. For example, a line chart is ideal for showcasing website traffic over time, while a pie chart effectively represents the distribution of traffic sources. Bar charts are excellent for comparing metrics across different categories, such as different marketing campaigns or geographic locations. Remember to choose the chart type that best represents your data and the message you want to convey.
Avoid cluttering visualizations with too much data; focus on highlighting the most important insights. Clear and concise labels, titles, and legends are crucial for readability.
Best Practices for Presenting GA4 Data to Stakeholders
Presenting GA4 data effectively requires tailoring your communication to your audience. For executive-level stakeholders, focus on high-level summaries and key performance indicators (KPIs). Use clear, concise language, avoiding technical jargon. For more technical audiences, you can delve deeper into the data, providing more granular analysis and exploring underlying trends. Always begin with a clear explanation of the context and the objectives of the report.
End with clear, actionable recommendations based on the data presented. Consider using a narrative approach, telling a story with your data to make it more engaging and memorable.
Sample GA4 Performance Report
This sample report focuses on key website performance indicators over the past month.
| Metric | Value | Trend (vs. Previous Month) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Users | 15,000 | +10% | Significant increase, possibly due to successful marketing campaign |
| New Users | 8,000 | +15% | Strong growth in new user acquisition |
| Average Session Duration | 2 minutes 30 seconds | +5% | Improved engagement |
| Bounce Rate | 30% | -5% | Reduction in bounce rate suggests improved content relevance |
| Conversion Rate | 5% | +2% | Positive improvement in conversion rate |
| Top Acquisition Channels | Organic Search (40%), Social Media (30%), Paid Search (20%), Email (10%) | – | Organic search remains the primary driver of traffic |
This report provides a concise overview of website performance, highlighting key trends and offering insights into areas for improvement. It is structured for easy understanding and includes clear interpretations of the data. The inclusion of trend analysis allows for easy identification of positive or negative changes over time.
Tips for Creating Clear and Concise GA4 Reports
Creating effective GA4 reports requires careful planning and execution. Here are some key tips:
Before diving into data visualization, define your objectives. What specific questions are you trying to answer with this report? What key performance indicators (KPIs) are most relevant to your business goals? A clear understanding of your objectives will guide your data selection and visualization choices.
- Focus on key metrics: Don’t overwhelm your audience with too much data. Select only the most relevant metrics to tell your story.
- Use clear and concise language: Avoid jargon and technical terms that your audience may not understand.
- Visualize data effectively: Choose the right chart type for your data and ensure that your visualizations are easy to understand.
- Tell a story with your data: Don’t just present the data; explain what it means and what actions should be taken.
- Provide context: Explain the time period covered by the report and any relevant factors that may have influenced the results.
- Include clear recommendations: Based on your analysis, provide actionable recommendations for improvement.
Summary: Google Analytics 4 Takeover What You Need To Know
The shift to Google Analytics 4 is significant, but it also presents incredible opportunities to gain deeper insights into your website’s performance. By understanding the core differences between UA and GA4, mastering the new interface, and utilizing its advanced features, you can unlock a wealth of data-driven knowledge. Don’t be intimidated by the change – embrace it! With the right knowledge and a proactive approach, you can successfully navigate this transition and gain a competitive edge in the ever-evolving world of digital analytics.
So, dive in, explore GA4, and watch your website analytics reach new heights!
FAQ Insights
What happens if I don’t migrate to GA4 before the UA deadline?
You’ll lose access to your historical UA data after the sunset date. This means you’ll no longer be able to track and analyze your website’s performance using UA.
Is GA4 more difficult to learn than UA?
While there’s a learning curve, GA4’s event-based data model offers a more holistic view of user behavior. Many find the initial adjustment challenging, but the long-term benefits outweigh the initial effort.
Can I use GA4 and UA simultaneously?
Yes, you can run both GA4 and UA properties concurrently during the transition period. This allows you to compare data and gradually adapt to the new platform.
How much does GA4 cost?
GA4 is a free tool provided by Google.
