Digital vs Print Marketing Which Reigns Supreme?
Digital vs print marketing – it’s the age-old question facing businesses today. Both offer unique advantages, but choosing the right approach (or a smart blend of both!) is crucial for success. This post dives deep into the core differences, exploring reach, cost, measurement, and creative considerations. We’ll weigh the pros and cons, helping you navigate this marketing maze and ultimately choose the strategy that best aligns with your goals and budget.
Get ready to uncover the secrets to effective marketing in the modern world!
From the targeted precision of digital campaigns to the tangible impact of print, we’ll examine how each medium can contribute to a comprehensive marketing strategy. We’ll explore the exciting possibilities of combining these approaches for maximum impact, showcasing real-world examples of integrated campaigns that have yielded remarkable results. By the end of this journey, you’ll have a clearer understanding of which path – or combination of paths – will lead your brand to triumph.
Reach and Targeting: Digital Vs Print Marketing
Choosing between digital and print marketing often hinges on understanding your target audience and the best way to reach them. While both methods have their strengths, their reach and targeting capabilities differ significantly, impacting campaign effectiveness and overall return on investment. This section will delve into a comparison of reach and targeting options for each, highlighting the unique advantages and limitations of each approach.
Digital and print marketing offer distinct approaches to reaching potential customers. Print marketing, with its reliance on physical media, traditionally faces limitations in geographic reach and precise audience targeting. Digital marketing, however, leverages the internet’s vast network to achieve broader reach and highly targeted campaigns. Let’s explore these differences in more detail.
Reach and Geographic Limitations
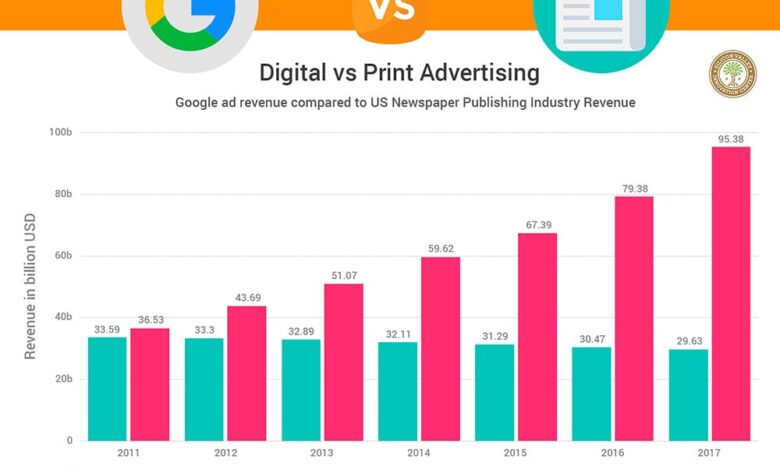
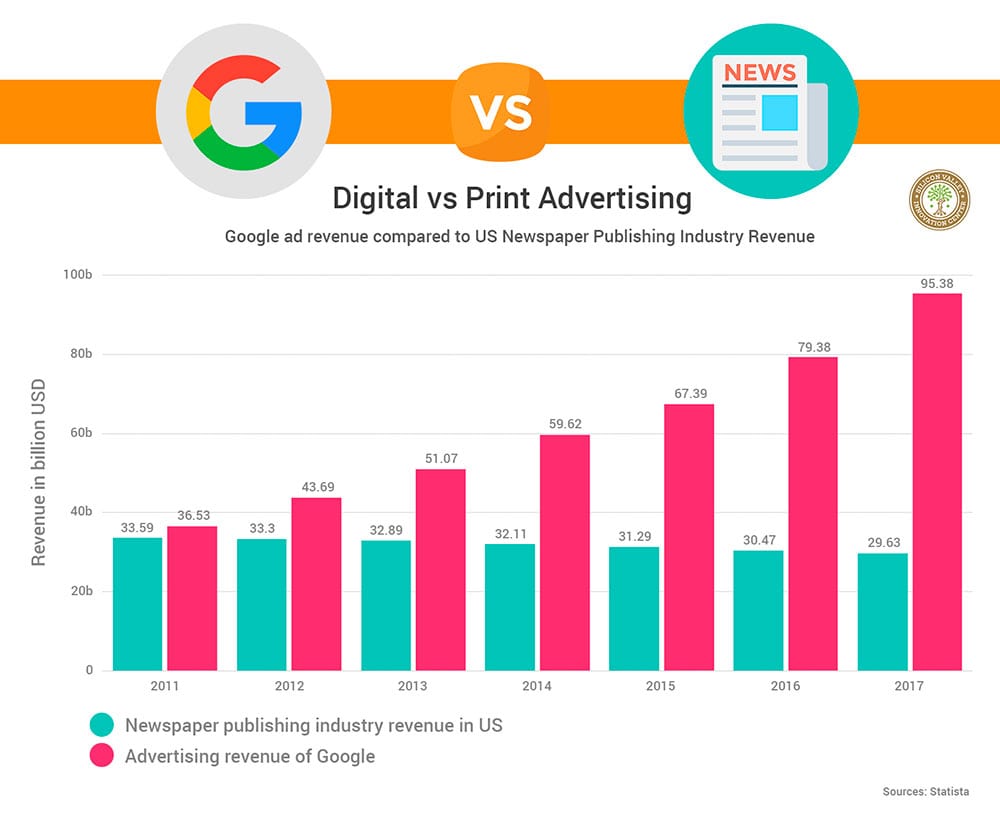
Print marketing, encompassing mediums like newspapers, magazines, and brochures, typically has a geographically limited reach. A local newspaper ad, for instance, primarily targets readers within a specific city or region. National print campaigns require significant investment across multiple publications to achieve wider coverage, but even then, reaching a truly diverse national audience can be challenging and expensive. Conversely, digital marketing transcends geographical boundaries.
A well-optimized website or social media campaign can reach a global audience instantaneously. However, the actual
-effective* reach depends on factors like language, cultural relevance, and the platform used. For example, a Facebook campaign targeting English speakers will have a different reach than one targeting Mandarin speakers.
Targeting Capabilities Comparison
| Feature | Digital Marketing | Print Marketing |
|---|---|---|
| Geographic Targeting | Highly precise (down to zip code, city, or even specific interests within a region) | Limited, often regional or national; less precise targeting. |
| Demographic Targeting | Highly precise (age, gender, income, education, interests, etc.) using various data sources and platform capabilities. | Limited; relies on publication demographics (e.g., reader profiles for magazines) which may be broad or outdated. |
| Behavioral Targeting | Highly precise (website browsing history, purchase history, app usage, etc.) allowing for retargeting and personalized ads. | Limited; relies on inferred behaviors based on publication readership or self-reported data from surveys (which may not be accurate). |
| Custom Audience Targeting | Highly customizable; allows for targeting specific user lists based on email addresses, phone numbers, or other identifiers. | Limited; options are typically broad and lack the granular control offered by digital platforms. |
Unique Digital Targeting Options
Digital marketing offers several unique targeting options unavailable in print. Retargeting, for example, allows advertisers to re-engage users who have previously interacted with their website or ads. This is highly effective in driving conversions. Behavioral targeting uses data about user online behavior (browsing history, search queries, etc.) to show highly relevant ads. For example, someone who searches for “best running shoes” online might see targeted ads for running shoes from various brands on different websites and social media platforms.
This level of precision is unmatched in print marketing.
Measuring Campaign Reach
Measuring campaign reach also differs significantly. Digital marketing offers robust analytics platforms (Google Analytics, social media insights, etc.) that provide detailed data on impressions, clicks, website traffic, conversions, and other key metrics. This allows for real-time monitoring and optimization of campaigns. In contrast, measuring the reach of print campaigns is more challenging and often relies on estimates based on circulation figures, readership surveys, and brand awareness studies.
While these methods provide some insights, they lack the precision and granularity of digital analytics.
Cost and Budget
Choosing between digital and print marketing often comes down to budget. Both offer unique advantages, but understanding the cost structure of each is crucial for effective campaign planning. While a precise cost comparison is impossible without specific campaign details, we can examine typical expenses and influencing factors to help you make an informed decision.
The cost of marketing isn’t just about the initial investment; it’s about the ongoing expenses and the return you get on that investment. Let’s break down the typical cost elements for both digital and print marketing.
Cost Breakdown for Digital and Print Marketing
The following lists Artikel the typical costs associated with each marketing approach. Remember that these are estimates and can vary significantly based on factors like campaign scope, target audience, and desired results.
- Digital Marketing:
- Creation Costs: Website design and development, content creation (blog posts, articles, videos, infographics), social media graphic design, email template design. Costs can range from a few hundred dollars for basic content to thousands for complex website development and professional video production. For example, a simple social media campaign might cost a few hundred dollars for graphic design, while a complex video marketing campaign could cost thousands.
- Distribution Costs: Pay-per-click (PPC) advertising (Google Ads, social media ads), social media management tools, email marketing platforms. PPC campaigns can range from a few dollars a day to thousands depending on targeting and bidding strategies. Social media management tools typically involve monthly subscriptions, while email marketing platforms offer various pricing tiers.
- Measurement Costs: Analytics tools (Google Analytics), social media analytics dashboards. Many analytics tools are free, but advanced features often require paid subscriptions. The cost is usually minimal, compared to creation and distribution.
- Print Marketing:
- Creation Costs: Design and layout of brochures, flyers, print ads, etc. Professional design services can range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars depending on complexity and quantity. Simple flyer design might cost a few hundred, while a complex brochure design could be significantly more.
- Distribution Costs: Printing costs (number of copies, paper quality, finishing), postage, distribution channels (direct mail, newspaper/magazine ads). Printing costs vary greatly depending on the quantity and quality of the print material. Postage and distribution can add a substantial amount to the overall cost, particularly for large-scale direct mail campaigns.
- Measurement Costs: Tracking response rates (coupons, unique codes), surveys, focus groups. These methods can be costly, particularly for large-scale campaigns. Tracking response rates may involve manual data entry or the use of specialized software.
Factors Influencing Marketing Budgets
Several factors significantly impact the overall budget for both digital and print marketing. Understanding these factors is crucial for accurate budget allocation.
- Campaign Goals and Objectives: Ambitious campaigns with broad reach and complex objectives will naturally require larger budgets than smaller, more focused campaigns. For example, a nationwide brand awareness campaign will be far more expensive than a local promotion.
- Target Audience: Reaching specific demographics or niche audiences can significantly influence costs. Highly targeted digital advertising campaigns can be more expensive than broader, less targeted print campaigns.
- Campaign Duration: Longer campaigns naturally require larger budgets than shorter campaigns. A year-long digital marketing campaign will cost more than a one-month campaign.
- Creative Resources: High-quality creative assets (photography, videography, design) significantly impact costs. Professionally produced videos and high-resolution images are more expensive than amateur content.
Return on Investment (ROI) Comparison
Comparing the ROI of digital and print marketing requires careful consideration of different metrics. While precise ROI calculation is campaign-specific, some general observations can be made.
Digital marketing often offers better opportunities for precise tracking and measurement, leading to a clearer understanding of ROI. Metrics like website traffic, conversion rates, and click-through rates provide valuable data for optimizing campaigns and demonstrating return on investment. Print marketing, on the other hand, often relies on less precise metrics like response rates and brand awareness surveys, making ROI assessment more challenging.
Digital marketing, with its detailed tracking capabilities, generally offers a more easily measurable ROI, while print marketing’s ROI can be more difficult to quantify directly.
Ultimately, the best marketing approach depends on your specific goals, target audience, and budget. A blended approach, combining digital and print strategies, can often yield the best results.
Measurement and Analytics

Source: 84signshop.com
Measuring the success of your marketing campaigns, whether digital or print, is crucial for optimizing your strategy and maximizing your return on investment (ROI). Understanding the key performance indicators (KPIs) and utilizing the right analytics tools are essential for making data-driven decisions and improving future campaigns. This section will delve into the specific metrics and tools used to track and interpret results for both digital and print marketing.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Digital and Print Marketing
Choosing the right KPIs depends heavily on your overall marketing objectives. However, some metrics are consistently valuable across both digital and print. The table below highlights key differences in how these KPIs are measured and interpreted across the two channels.
| KPI | Digital Marketing Measurement | Print Marketing Measurement | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reach | Website traffic, social media engagement, email open rates, ad impressions | Circulation numbers, readership surveys, geographic distribution data | Indicates the size of your audience and the potential impact of your campaign. Higher reach generally suggests greater brand awareness. |
| Engagement | Click-through rates (CTR), time on site, social media shares, comments, likes | Response rates to coupons or offers, website visits from print ads (tracked via unique URLs or QR codes), reader surveys measuring recall and brand awareness | Measures how actively your audience interacts with your message. High engagement suggests a resonant campaign. |
| Conversion Rate | Sales, leads generated, form submissions, app downloads | Coupon redemption rates, sales inquiries from print ads, direct response to print advertisements (e.g., phone calls, mail-in forms) | Shows how effectively your campaign drives desired actions. A higher conversion rate indicates a successful campaign in achieving its goals. |
| Return on Investment (ROI) | Calculated by comparing the cost of the campaign to the revenue generated | Calculated by comparing the cost of the campaign to the increase in sales or other quantifiable results. This often requires more complex attribution modeling. | The ultimate measure of success. A positive ROI indicates profitability. |
Tools and Techniques for Tracking and Analyzing Results
Digital marketing offers a wealth of readily available tools for tracking and analyzing campaign performance. Print marketing, however, requires more creative solutions to measure impact.Digital marketing utilizes platforms like Google Analytics, social media analytics dashboards (Facebook Insights, Twitter Analytics), and marketing automation tools (HubSpot, Marketo) to track website traffic, user behavior, conversion rates, and campaign ROI. These tools provide detailed data visualizations and reports, allowing marketers to easily monitor performance in real-time.
A/B testing is also commonly used to optimize campaign elements.Measuring the success of print campaigns often relies on more indirect methods. This can include tracking unique URLs or QR codes in print advertisements to redirect users to a landing page where their actions can be tracked, conducting surveys to assess brand awareness and recall, analyzing sales data correlated with print advertising campaigns, and using coupon codes to trace conversions back to specific print materials.
Interpreting Data from Different Measurement Methods
Interpreting data requires a critical eye and a holistic view. For digital marketing, analyzing website traffic patterns, user engagement metrics, and conversion funnels provides insights into campaign effectiveness. For instance, a low click-through rate on a digital ad might suggest the need for improved ad copy or targeting. Conversely, high bounce rates might point to poor website design or irrelevant content.Print marketing data interpretation often involves correlating sales data with the timing and reach of print campaigns.
For example, a noticeable sales increase following a print advertisement campaign in a specific region suggests a positive correlation. However, attributing sales solely to print advertising can be challenging, and it is important to consider other factors that might influence sales, such as seasonality or competitor activity. Qualitative data from surveys can provide additional context and insight into brand awareness and customer perception.
Content Creation and Design
Source: inkbotdesign.com
The creative process behind digital and print marketing materials, while sharing some common ground, diverges significantly in its approach and execution. Print design prioritizes a static, visually compelling presentation optimized for a tangible medium, whereas digital design emphasizes interactivity and adaptability across various screen sizes and platforms. This fundamental difference influences every stage of the creative process, from initial concept to final delivery.Digital and print design necessitate distinct creative considerations.
Print materials must account for the limitations of the printing process, including color accuracy, paper stock, and the overall physical dimensions. Digital design, conversely, needs to adapt to the ever-changing landscape of screen resolutions, browser compatibility, and the need for responsive design to ensure optimal viewing across different devices. The inherent interactivity possible in digital marketing – through animations, videos, and clickable elements – is entirely absent in the static world of print.
Design Considerations for Different Media
Print design prioritizes high-resolution images and crisp typography to ensure readability and visual appeal in a physical format. The color palette is often carefully selected to complement the chosen paper stock and create a cohesive brand experience. Consider a high-end brochure for a luxury car manufacturer; the paper stock might be thick, glossy, and the images would be meticulously retouched for exceptional clarity.
The typography would be elegant and sophisticated, reflecting the brand’s image. In contrast, digital design necessitates a focus on responsive design principles, ensuring the material looks good on a desktop, tablet, or smartphone. File sizes need to be optimized for fast loading times, and the use of animation and interactive elements can enhance user engagement. Imagine a digital banner ad for the same luxury car; it would utilize high-quality, but compressed images to ensure quick loading.
The text would be concise and impactful, optimized for readability at various screen sizes, and might include an animation showcasing the car’s features.
Headline Creation for Print and Digital
Creating compelling headlines for print and digital advertisements requires different approaches. Print headlines often benefit from a more descriptive and slightly longer approach, aiming to capture attention in a less cluttered environment. The headline needs to stand alone, compelling the reader to delve into the body copy. A print advertisement for a new coffee blend might use a headline like: “Indulge in the Rich Aroma of Ethiopian Yirgacheffe: A Symphony of Flavors Awaits.” This headline is descriptive, evocative, and creates a sense of luxury.
Digital headlines, on the other hand, must be concise and impactful, often needing to convey the message quickly to grab attention in a fast-paced, information-saturated environment. A digital banner ad for the same coffee might use a headline like: “Ethiopian Yirgacheffe: Taste the Difference.” This is short, punchy, and focuses on the key benefit. The limited space and the need for immediate impact are paramount considerations.
Engagement and Interaction
The way consumers engage with marketing materials differs drastically between the digital and print worlds. Digital marketing offers immediate, interactive experiences, while print relies on more passive engagement, though it can still be surprisingly effective. Understanding these differences is crucial for optimizing campaigns and achieving marketing goals. The level of interaction directly impacts brand perception and ultimately, sales.Digital and print marketing present distinct opportunities for consumer interaction and feedback.
Digital channels offer a range of interactive features fostering immediate responses and fostering a sense of community. Print, while less immediately interactive, can still encourage engagement through cleverly designed call-to-actions, such as QR codes linking to online resources or contests.
Digital Engagement Methods
Digital marketing thrives on interaction. Consumers engage through clicks, shares, likes, comments, and participation in online communities. This active engagement allows for immediate feedback, enabling marketers to quickly adjust strategies based on real-time data. For example, a social media post’s engagement metrics (likes, shares, comments) directly inform future content strategy. Email marketing allows for tracking open rates, click-through rates, and conversions, providing valuable insights into consumer interest and campaign effectiveness.
Interactive content like quizzes, polls, and games further boost engagement and data collection.
Print Engagement Methods
While seemingly less dynamic, print marketing can still achieve high levels of engagement. High-quality print materials, such as brochures with striking visuals and clear messaging, can create a lasting impression. Tactile elements, like textured paper or unique finishes, enhance the sensory experience. Clever use of white space and compelling visuals can hold attention and encourage careful reading.
Including QR codes linking to online content bridges the gap between print and digital, enabling a multi-channel approach to engagement. Contests and promotions using unique codes printed on materials can also drive engagement and data collection. For example, a beautifully designed magazine advertisement with a QR code linking to a product discount can lead to direct sales and data capture.
User Experience (UX) in Digital Marketing and Print Design
User experience (UX) in digital marketing focuses on creating intuitive and enjoyable online experiences. This involves aspects like website navigation, mobile responsiveness, page load speed, and overall site aesthetics. A positive UX leads to increased engagement and conversions. For example, a website with a clear call to action and easy navigation will encourage more purchases than a confusing, slow-loading site.
In print design, the equivalent of UX is the overall design and readability. This encompasses aspects like typography, layout, use of color, and image selection. A well-designed brochure with clear messaging and visually appealing layout is more likely to capture and maintain a reader’s attention than a poorly designed one. For instance, a brochure with a cluttered layout and small, hard-to-read font will likely be discarded, whereas a clean, visually appealing brochure will be more likely to be read and retained.
Examples of Successful Campaigns
Blending digital and print marketing effectively can create powerful campaigns that resonate with audiences across multiple touchpoints. The key is strategic integration, not simply using both channels independently. Successful campaigns often leverage the strengths of each medium to create a cohesive and impactful message. Let’s explore some examples and then delve into a hypothetical integrated campaign.
Successful Integrated Marketing Campaigns
Several successful campaigns demonstrate the power of combining digital and print strategies. Understanding the specific elements, target audience, and results achieved in these campaigns provides valuable insights for developing your own integrated approach.
- Dove’s Real Beauty Campaign: This campaign utilized print advertisements featuring diverse women, challenging traditional beauty standards. Digitally, they leveraged social media to encourage user-generated content and conversations around body positivity. The campaign’s target audience was women of all ages and backgrounds. Results included increased brand awareness, positive brand sentiment, and significant sales growth. The print ads provided a powerful visual impact, while the digital aspect fostered community and engagement.
- Burberry’s Social Media and Print Collaboration: Burberry cleverly integrated print and digital by featuring the same models and imagery in both their print campaigns and social media posts. This created a cohesive brand identity across channels. The target audience was affluent young adults interested in fashion and luxury goods. The campaign achieved increased brand visibility and engagement across platforms, driving sales and strengthening brand loyalty.
The consistent branding across media amplified the message’s impact.
- Starbucks’ “Meet Me at Starbucks” Campaign: This campaign used print ads in magazines and newspapers featuring cozy scenes of people connecting at Starbucks locations, while simultaneously using social media to promote similar themes and encourage customers to share their own “Starbucks moments.” The target audience was a broad demographic encompassing various age groups and lifestyles. The integrated campaign successfully increased foot traffic to Starbucks locations and strengthened the brand’s association with community and connection.
The combination of aspirational print imagery and relatable digital engagement created a compelling narrative.
Hypothetical Integrated Marketing Campaign: Local Coffee Shop, Digital vs print marketing
Let’s imagine a hypothetical campaign for a new, locally-owned coffee shop called “The Daily Grind.”
Campaign Objectives: To increase brand awareness within a 5-mile radius, drive foot traffic to the shop during its opening month, and establish a loyal customer base.
So, digital vs print marketing – it’s a constant debate, right? Print’s tangible, digital’s viral. But to really nail digital success, you need a strong video strategy, and that’s where learning how to leverage YouTube comes in. Check out this awesome guide on getting it on with YouTube to boost your reach. Ultimately, a blended approach – smart print campaigns alongside a killer YouTube presence – often yields the best results in today’s diverse marketing landscape.
Target Audience: Local residents (ages 25-55) who appreciate high-quality coffee, a comfortable atmosphere, and supporting local businesses. This includes professionals, students, and families within the local community.
Integrated Strategy Rationale: We’ll use print and digital to complement each other. Print offers a tangible, localized reach, while digital allows for targeted advertising and engagement.
- Print: Flyers distributed to nearby businesses, homes, and community centers. Advertisements in local newspapers and community magazines featuring high-quality images of the coffee shop’s ambiance and signature drinks. A loyalty card included with print materials.
- Digital: Targeted Facebook and Instagram ads showcasing the coffee shop’s unique offerings and atmosphere. A website with online ordering capabilities and a blog featuring local events and coffee-related content. Geo-targeted ads on Google My Business to reach customers searching for coffee shops nearby. Social media contests and giveaways to encourage engagement and build community.
This integrated approach ensures a consistent brand message across platforms while maximizing reach and engagement with the target audience. The print materials provide a physical reminder and build local credibility, while the digital strategy allows for precise targeting and real-time engagement.
Future Trends
The marketing landscape is in constant flux, with digital and print media evolving at different paces yet increasingly influencing each other. Understanding the emerging trends in both realms is crucial for businesses aiming to remain competitive and connect effectively with their target audiences. This section explores the future trajectory of digital and print marketing, highlighting potential challenges and opportunities.
The Rise of AI in Digital Marketing
Artificial intelligence is rapidly transforming digital marketing, automating tasks, personalizing experiences, and enhancing targeting accuracy. AI-powered tools analyze vast datasets to predict consumer behavior, optimize ad campaigns, and personalize website content. For example, Netflix utilizes AI to suggest shows based on viewing history, demonstrating the power of AI-driven personalization. This trend presents opportunities for increased efficiency and ROI, but also challenges related to data privacy and algorithmic bias which need careful consideration and ethical implementation.
Print’s Continued Niche and Sustainability Focus
While digital marketing dominates the conversation, print media isn’t disappearing. Instead, it’s finding its niche in high-quality, tactile experiences that offer a unique brand interaction. Luxury brands, for instance, often leverage print for packaging and exclusive collateral to create a sense of exclusivity and permanence. Furthermore, a growing focus on sustainability within the print industry is leading to the use of recycled materials and eco-friendly printing processes, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers.
This shift presents opportunities for brands to communicate their values and create a lasting impression, while the challenges lie in balancing cost-effectiveness with eco-friendly practices.
The Convergence of Digital and Print
We are seeing an increasing integration of digital and print marketing strategies. QR codes embedded in print materials can direct consumers to online content, creating a seamless omnichannel experience. Similarly, personalized print pieces can be triggered by digital interactions, such as targeted emails leading to customized brochures. For example, a real estate company might send a personalized property brochure based on a user’s online search history, combining the personalized appeal of digital with the tangible quality of print.
This convergence offers opportunities for enhanced customer engagement and a more holistic brand experience, while the challenge lies in coordinating and measuring the effectiveness of these integrated campaigns effectively.
Augmented Reality and Immersive Experiences
Augmented reality (AR) is poised to revolutionize both digital and print marketing. AR overlays digital information onto the real world, creating interactive experiences that can be incorporated into print materials or digital campaigns. Imagine scanning a magazine advertisement with a smartphone to view a 3D model of the product or experience an interactive product demonstration. This offers incredible opportunities for immersive brand storytelling and product demonstrations, but presents challenges in terms of technical development and user accessibility.
The Importance of Data Privacy and Ethical Considerations
With the increasing reliance on data in both digital and print marketing, data privacy and ethical considerations are becoming paramount. Consumers are becoming more aware of how their data is collected and used, demanding transparency and control over their personal information. This necessitates a shift towards ethical data practices and a focus on building trust with consumers. Companies that prioritize data privacy and ethical marketing will be better positioned for long-term success, while those that fail to do so risk reputational damage and legal repercussions.
The challenge here lies in balancing the need for data-driven insights with the ethical responsibility of protecting consumer privacy.
Closing Notes
Ultimately, the “best” marketing approach isn’t a one-size-fits-all answer. Digital and print marketing each possess unique strengths, and a successful strategy often involves a strategic combination of both. By understanding the nuances of each, analyzing your target audience, and carefully considering your budget and goals, you can craft a marketing plan that delivers exceptional results. Remember to track your KPIs, adapt your strategy based on data, and embrace the ever-evolving landscape of the marketing world.
The journey is just as important as the destination – so let’s get started!
FAQ Guide
What’s the best way to measure the success of a print marketing campaign?
Tracking print campaign success often involves using unique URLs, QR codes, or discount codes specific to the print material. Monitor website traffic, sales conversions, and customer inquiries linked to these unique identifiers.
How can I integrate digital and print marketing effectively?
Integrate by using print ads to drive traffic to your website or social media. Include QR codes in print materials linking to online resources. Use consistent branding and messaging across both platforms.
What are some emerging trends in print marketing?
Personalized print, direct mail with augmented reality elements, and sustainable print practices are all growing trends.
Is print marketing dead?
Absolutely not! While digital marketing has exploded, print still holds a significant place, particularly for building brand awareness and creating a tangible connection with customers.