How to Use Localization and Internationalization to Expand Your Global Customer Base
How to use localization and internationalization to expand your global customer base? It’s a question on every ambitious business owner’s mind. Going global isn’t just about translating your website; it’s about deeply understanding your target audiences, adapting your product to resonate with their culture, and navigating the legal landscape of international markets. This journey requires careful planning, strategic execution, and a willingness to embrace cultural nuances.
Get ready to discover how to unlock a world of new customers and take your business to the next level!
This post will guide you through the essential steps, from initial market research and cultural sensitivity training to the technical implementation of multilingual support and the ongoing monitoring of your global success. We’ll explore the differences between localization and internationalization, delve into the crucial aspects of a winning internationalization strategy, and even provide practical examples and case studies to illustrate best practices.
By the end, you’ll have a clear roadmap to navigate the exciting and sometimes challenging world of global expansion.
Understanding Localization and Internationalization
Going global is a thrilling prospect for any business, but successfully reaching international markets requires more than just translating your website. It necessitates a deep understanding of both internationalization and localization – two distinct but interconnected processes. Mastering these will unlock the potential of a truly global customer base.Internationalization and localization are often used interchangeably, but they represent different stages in the process of adapting your product or service for global audiences.
Internationalization is the design and development process that makes your product adaptable to different locales without engineering changes. Localization, on the other hand, is the process of adapting your product to a specific target market, taking into account cultural nuances, language, and local regulations. Think of internationalization as building a house with adaptable rooms, while localization is furnishing and decorating those rooms to suit specific tenants.
Internationalization Strategy Key Aspects
A successful internationalization strategy requires careful planning and execution. It’s not a one-size-fits-all approach; it needs to be tailored to your specific product, target markets, and resources. Key aspects include identifying your target markets, conducting thorough market research, developing a flexible and scalable architecture, and establishing a robust translation workflow. Ignoring any of these can lead to significant challenges and missed opportunities.
Step-by-Step Guide for Planning Internationalization
Planning for internationalization is crucial. A well-defined plan helps ensure smooth execution and minimizes potential roadblocks. Consider this step-by-step guide:
- Market Research: Identify your target markets, analyze their demographics, cultural preferences, and linguistic needs. For example, research on the preferences of Japanese consumers will differ greatly from that of Brazilian consumers.
- Product Assessment: Evaluate your product’s suitability for international markets. Are there any features that may be culturally insensitive or legally problematic in certain regions? For example, a dating app may need to adapt its features to comply with different countries’ privacy laws.
- Technical Planning: Design your product with internationalization in mind. This involves using Unicode encoding, separating text from code, and designing a flexible architecture that can easily accommodate different languages and currencies. For example, consider using a database to store translatable text rather than hardcoding it.
- Resource Allocation: Allocate sufficient resources (budget, personnel, time) to the internationalization process. Underestimating the effort required can lead to delays and compromises in quality.
- Testing and Feedback: Thoroughly test your product in different locales to identify and fix any issues before launch. Gather feedback from native speakers in your target markets.
Product Readiness for Localization Checklist
Before embarking on localization, it’s essential to ensure your product is ready. This checklist helps identify potential issues:
- Unicode Support: Does your application support Unicode characters?
- Externalizable Strings: Are all strings and text easily extractable for translation?
- Date/Time/Number Formatting: Does your application use locale-independent formatting for dates, times, and numbers?
- Currency Support: Can your application handle different currencies and currency symbols?
- Right-to-Left Language Support: Does your application support right-to-left languages like Arabic and Hebrew?
- Image and Media Localization: Are images and other media culturally appropriate for all target markets?
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Does your application comply with all relevant laws and regulations in your target markets?
Market Research and Target Audience Analysis: How To Use Localization And Internationalization To Expand Your Global Customer Base
Expanding your business globally requires more than just translating your website. A deep understanding of your target markets is crucial for successful internationalization. This involves meticulous market research and a nuanced analysis of cultural differences to ensure your product resonates with its intended audience. Ignoring these factors can lead to costly mistakes and missed opportunities.Market research for international expansion goes beyond simple demographics.
It necessitates a comprehensive understanding of cultural nuances, consumer behaviors, and local market dynamics. This includes identifying key cultural considerations that can influence purchasing decisions, brand perception, and marketing strategies. Analyzing these factors allows businesses to tailor their products and marketing messages to effectively engage with diverse customer segments worldwide.
Cultural Considerations for Different Target Markets
Understanding cultural nuances is paramount for successful global marketing. These nuances impact everything from color choices and imagery to messaging and product features. For example, what’s considered auspicious in one culture might be offensive in another. Similarly, humor, symbolism, and even the preferred communication style can vary dramatically across regions. Thorough research helps businesses avoid misinterpretations and cultural faux pas that can damage brand reputation and hinder sales.
Comparing Global Customer Segment Needs and Preferences
Global customer segments, even within the same geographical region, exhibit diverse needs and preferences. For instance, the preferences of a young, urban consumer in Tokyo might differ significantly from those of a rural consumer in the same country. Similarly, price sensitivity, product features valued, and preferred communication channels can all vary greatly depending on demographic factors like age, income, and lifestyle.
Analyzing these differences allows for the creation of targeted marketing campaigns and product variations that cater to specific customer needs.
Cultural Nuances Relevant to Product Localization
| Culture | Language | Visuals/Imagery | Product Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | English (various dialects) | Focus on individuality, freedom, and progress; bright, bold colors. | Emphasis on convenience, innovation, and technological advancements. |
| Japan | Japanese | Subtlety, harmony, and nature-inspired imagery; pastel colors. | High quality, attention to detail, and sophisticated design. |
| Germany | German | Order, precision, and functionality; clean lines and muted colors. | Reliability, durability, and technical specifications are highly valued. |
| Brazil | Portuguese | Vibrant colors, strong family ties, and celebrations; focus on emotional connections. | Value for money, strong customer service, and social responsibility are key considerations. |
Examples of Successful and Unsuccessful International Marketing Campaigns
Successful campaigns often leverage deep cultural understanding. For example, Coca-Cola’s consistent global branding, while adapting its marketing messages to local cultural contexts, has been remarkably successful. Conversely, examples of unsuccessful campaigns often highlight a lack of cultural sensitivity. A notable example is the infamous Pepsi commercial featuring Kendall Jenner, which was widely criticized for trivializing social justice movements and misrepresenting cultural sensitivities.
These examples highlight the critical importance of conducting thorough market research and ensuring cultural appropriateness in all marketing materials.
Translating and Adapting Content
Successfully reaching a global audience requires more than just translating your website; it demands a deep understanding of cultural nuances and effective adaptation of your marketing materials. Simply swapping words isn’t enough; you need to resonate with your target audience on an emotional level. This section explores the critical steps of translating and adapting content for international markets.
Professional translation services are invaluable for ensuring accuracy and cultural appropriateness. While machine translation tools can be helpful for initial drafts, they often lack the nuanced understanding of idioms, colloquialisms, and cultural context that a human translator possesses. Relying solely on machine translation can lead to misinterpretations, awkward phrasing, and even offensive content, ultimately damaging your brand image and hindering your global expansion efforts.
The Challenges of Translating Marketing Materials
Translating marketing materials presents unique challenges due to the creative and persuasive nature of the content. Direct translations often fail to capture the intended meaning or emotional impact. For example, a catchy slogan in one language might sound clunky or meaningless in another. Furthermore, different languages have varying sentence structures and word lengths, which can impact the overall layout and design of your marketing materials.
Humor, in particular, is notoriously difficult to translate effectively, as what is considered funny in one culture might be offensive or incomprehensible in another. Therefore, a deep understanding of the target language and culture is essential for successful translation.
Best Practices for Adapting Marketing Materials to Local Cultures
Adapting marketing materials goes beyond simple translation; it involves modifying content to resonate with local cultural values, preferences, and norms. This might involve adjusting colors, imagery, and even the overall message to align with local sensitivities. For instance, a marketing campaign featuring a specific animal might be well-received in one culture but considered taboo or unlucky in another.
Similarly, certain color schemes or symbols can hold different meanings across cultures. Thorough market research is crucial to understand these nuances and avoid potential cultural faux pas. This ensures your marketing efforts are not only understood but also well-received and effective.
Utilizing Translation Management Systems
Translation management systems (TMS) streamline the translation process, improving efficiency and consistency. A TMS centralizes all your translation projects, allowing you to manage terminology, track progress, and ensure consistent brand messaging across all languages. Features such as automated workflows, terminology databases, and quality assurance checks help minimize errors and maintain high-quality translations. Furthermore, a TMS can facilitate collaboration between translators, reviewers, and project managers, ensuring smooth communication and timely delivery of translated content.
Using a TMS significantly reduces the risk of inconsistencies and ensures your brand message remains consistent globally. Examples of popular TMS platforms include SDL Trados Studio, memoQ, and Across Language Server. These systems offer features such as translation memory to reuse previously translated segments, thereby reducing costs and improving efficiency.
Technical Considerations for Global Reach
Going global requires more than just translating your website; it demands a robust technical infrastructure capable of handling diverse languages, cultural nuances, and regional regulations. This section delves into the crucial technical aspects of internationalization and localization, ensuring your software and website are truly global-ready.
Website and App Design for Multilingual Support
Designing for multilingual support begins with careful planning. Avoid hardcoding text directly into your code. Instead, employ a resource file system, such as JSON or XML, to store your text strings separately. This allows for easy translation and updates without modifying the core code. Furthermore, consider using a Content Management System (CMS) with built-in multilingual capabilities, such as WordPress with plugins like WPML, or specialized CMS platforms designed for internationalization.
For apps, utilize frameworks that support internationalization, such as React’s `react-intl` or Angular’s `ngx-translate`. Properly structured databases are also key; storing translations in separate tables or columns, keyed to the language, ensures efficient retrieval and management.
Software Adaptation for Different Regions and Languages
Adapting software for various regions goes beyond just translation. Consider date and time formats, number formats (decimal separators, thousands separators), currency symbols, address formats, and even measurement units (metric vs. imperial). These regional differences require careful coding to ensure consistent and accurate display across all target markets. For example, a date format like “MM/DD/YYYY” in the US becomes “DD/MM/YYYY” in many European countries.
Failure to account for these variations can lead to data errors and user confusion. Robust testing with users from your target regions is essential to identify and address these nuances.
Potential Technical Challenges and Solutions
Internationalization and localization present several technical hurdles. One common challenge is character encoding. Using UTF-8 encoding ensures support for a wide range of characters from different languages, preventing garbled text. Another challenge involves right-to-left (RTL) languages like Arabic and Hebrew. Your website and app layout must adapt to accommodate RTL scripts, ensuring text flows correctly and UI elements are positioned appropriately.
This often requires adjustments to CSS and potentially even modifications to the underlying layout structure. Finally, handling different keyboard layouts and input methods is crucial for a positive user experience. Implementing input methods that accommodate different alphabets and character sets is essential for usability in diverse markets.
Technical Specifications for Global-Ready Software
Prioritizing global readiness from the initial design phase is crucial. Here’s a list of key technical specifications to consider:
- UTF-8 Encoding: All text should be encoded in UTF-8 to support a wide range of characters.
- Externalized Strings: All user-facing text should be stored in external resource files (e.g., JSON, XML).
- Locale-Aware Formatting: Implement locale-aware functions for dates, times, numbers, and currencies.
- Right-to-Left (RTL) Support: Ensure your UI adapts to RTL languages.
- Internationalized Keyboard Support: Support different keyboard layouts and input methods.
- Multilingual Database Design: Structure your database to efficiently manage translations.
- Comprehensive Testing: Thoroughly test your software in all target regions and languages.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Going global means navigating a complex web of international laws and regulations. Ignoring these legal intricacies can lead to hefty fines, reputational damage, and even legal battles that could severely hinder your business growth. Understanding and adhering to these regulations is crucial for sustainable international expansion.Legal implications for businesses expanding internationally are multifaceted and depend heavily on the specific countries targeted.
Different jurisdictions have varying laws concerning intellectual property, data privacy, consumer protection, taxation, and labor practices. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in significant legal and financial repercussions.
Data Privacy Regulations
Data privacy is a paramount concern in the digital age, and international businesses must understand and comply with diverse data protection laws across their target markets. The most prominent example is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, which mandates stringent rules on the collection, processing, and storage of personal data. Similar, though often less stringent, regulations exist in many other countries, including the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States and the Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL) in China.
Non-compliance can result in substantial fines and damage to brand reputation. For instance, a company failing to obtain explicit consent for data processing under GDPR could face fines of up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover, whichever is higher. Therefore, a comprehensive understanding of each relevant jurisdiction’s data protection laws is essential, necessitating the implementation of robust data privacy policies and procedures.
Examples of Legal Issues During Internationalization
Several real-world examples illustrate the potential legal pitfalls of international expansion. One common issue involves trademark infringement. A company might discover that its chosen brand name is already registered in another country, leading to costly legal battles to protect its intellectual property rights. Another frequent problem is related to contract law, where differences in legal systems can lead to disputes over contract interpretation and enforcement.
For example, a contract drafted under one country’s legal system might not be enforceable in another. Finally, differences in labor laws, including minimum wage, working hours, and employee benefits, can create significant challenges for companies operating across multiple jurisdictions. These examples underscore the importance of seeking legal counsel specializing in international business law to mitigate risks.
Reaching a global audience means speaking your customers’ language, literally! Proper localization and internationalization are key to expanding your business, and a big part of that is effective marketing. To really connect with your international viewers, you need a solid video strategy, which is why learning how to leverage YouTube is crucial; check out this great guide on getting it on with youtube to boost your reach.
By combining localized content with a strong YouTube presence, you’ll significantly increase your chances of success in the global market.
Legal Considerations for International Businesses
Before expanding internationally, businesses should carefully consider the following:
- Intellectual Property Rights: Registering trademarks, patents, and copyrights in each target market to protect intellectual property.
- Data Privacy Regulations: Implementing robust data privacy policies compliant with relevant laws in each jurisdiction (e.g., GDPR, CCPA, PIPL).
- Contract Law: Utilizing standardized international contract templates and seeking legal advice to ensure contracts are enforceable across borders.
- Taxation: Understanding and complying with tax laws in each country of operation, including VAT, corporate tax, and other relevant taxes.
- Labor Laws: Adhering to local labor laws concerning minimum wage, working hours, employee benefits, and termination procedures.
- Consumer Protection Laws: Complying with consumer protection laws concerning product safety, advertising, and warranties.
- Anti-Corruption Laws: Adhering to anti-bribery and anti-corruption laws, such as the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA) in the United States.
- Sanctions and Embargoes: Understanding and complying with international sanctions and embargoes that may affect business operations in certain countries.
Marketing and Distribution Strategies
Successfully expanding your global customer base requires a well-defined marketing and distribution strategy tailored to the nuances of each target market. Ignoring these cultural and logistical differences can lead to wasted resources and missed opportunities. A holistic approach, encompassing both localized marketing messages and efficient distribution channels, is crucial for achieving international success.
Global Marketing Plan Design, How to use localization and internationalization to expand your global customer base
A global marketing plan necessitates a detailed understanding of your target audiences across different regions. This includes not only demographic data but also psychographic factors such as cultural values, purchasing habits, and media consumption patterns. For example, a social media campaign heavily reliant on visual content might resonate well in a visually-oriented culture like South Korea, while a more text-based approach might be more effective in Germany.
The plan should Artikel specific marketing objectives for each region, detailing key performance indicators (KPIs) and outlining the budget allocation for each market. Consider A/B testing different marketing materials in various regions to optimize campaign effectiveness.
International Distribution Channels
Reaching international customers requires exploring various distribution channels. These could include e-commerce platforms like Amazon or Alibaba, which offer global reach, but require careful consideration of logistics and local regulations. Direct sales teams might be suitable for larger markets or high-value products, offering personalized service. Strategic partnerships with local distributors can provide valuable market access and knowledge, though it might involve relinquishing some control over pricing and distribution.
Finally, physical retail stores, while requiring significant investment, remain a crucial channel in many markets, particularly for tangible products. The optimal channel selection depends on factors like product type, target market, and budget constraints. For example, a software company might rely heavily on online distribution, while a food manufacturer might need a combination of online and offline channels.
Comparative Marketing Strategies Across Global Regions
Marketing strategies must adapt to the unique characteristics of each region. In North America, a focus on individualistic values and direct marketing approaches might be effective. Conversely, in collectivist cultures like Japan, emphasis on community and trust-building might be more successful. Consider the example of a luxury watch brand. In the US, an ad campaign might highlight the watch’s technical features and prestige.
In China, the same campaign might focus on the watch’s symbolic value and its association with social status and success. Marketing messages should be translated not just linguistically, but also culturally, ensuring they resonate with the local audience’s values and expectations.
Adapting Marketing Messages for Different Cultures
Cultural adaptation is paramount for successful global marketing. This goes beyond simple translation; it involves understanding and addressing cultural nuances in messaging, imagery, and even color schemes. For instance, the color white signifies purity and mourning in different cultures. Similarly, certain symbols or gestures might have positive connotations in one culture and negative ones in another. A thorough understanding of cultural sensitivities is essential to avoid misinterpretations and potential offense.
Employing local marketing teams or cultural consultants can greatly enhance the effectiveness of your global marketing efforts. For example, a food company launching a new product in India might need to adapt its packaging and marketing materials to reflect local tastes and preferences.
Measuring Success and Iteration

Source: theswissquality.ch
Successfully expanding into global markets requires more than just translation; it demands a robust system for tracking progress and adapting strategies. Understanding how your internationalization efforts are performing is crucial for optimizing your investment and maximizing your return. This involves carefully selecting Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), analyzing data effectively, and iterating your approach based on the insights gained.Measuring the success of your internationalization efforts requires a multifaceted approach.
You can’t rely on a single metric to paint a complete picture; instead, you need a combination of quantitative and qualitative data to understand the overall health of your global operations. This allows for a nuanced understanding of what’s working and what needs improvement.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for International Markets
Choosing the right KPIs is paramount. While the specific metrics will vary based on your business model and goals, some common indicators provide valuable insights. These metrics should be tracked consistently across all your international markets to allow for meaningful comparisons and analysis.
- Website Traffic and Engagement: Monitor website visits, bounce rates, time on site, and conversion rates from different regions. This reveals how effectively your localized content is attracting and engaging users.
- Sales and Revenue: Track sales figures, average order value (AOV), and revenue generated in each market. This provides a direct measure of your financial performance in each region.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Analyze the cost of acquiring a new customer in each market. This helps identify which markets are most efficient and which require optimization.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): Assess the long-term value of customers in each market. This helps prioritize markets with high potential for repeat business and loyalty.
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT): Measure customer satisfaction through surveys, feedback forms, and reviews. This offers valuable qualitative data to complement your quantitative findings.
Analyzing International Market Data
Once you’ve collected your data, the next step is to analyze it effectively. This involves more than just looking at individual numbers; it’s about identifying trends, patterns, and correlations.Consider using data visualization tools to present your findings clearly and concisely. Charts and graphs can effectively communicate complex data, making it easier to identify key trends and areas for improvement. For instance, a geographical heatmap could visually represent sales performance across different regions, instantly highlighting high-performing and underperforming areas.
Furthermore, comparing KPIs across different markets allows you to identify best practices and areas needing attention. For example, if your CAC is significantly higher in one market than others, it might indicate a need to adjust your marketing strategy in that specific region.
Adapting Strategies Based on Performance Data
Data analysis shouldn’t be a one-time event; it should be an ongoing process that informs your decision-making. Based on your findings, you can adjust your strategies to optimize performance.For example, if your website bounce rate is high in a particular market, it might suggest that your localized content isn’t resonating with the target audience. This could require revisiting your translation and adaptation process, potentially incorporating more culturally relevant elements.
Similarly, low conversion rates might necessitate improvements to your website design or checkout process, tailoring them to the specific preferences of the target market. By continuously monitoring and adapting your strategies based on performance data, you can ensure your internationalization efforts remain effective and efficient.
Sample Global Market Performance Report
| Market | Website Visits | Conversion Rate | Sales Revenue | CAC | CSAT Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | 100,000 | 5% | $500,000 | $5 | 4.5 |
| Canada | 50,000 | 3% | $150,000 | $10 | 4.0 |
| United Kingdom | 75,000 | 4% | $300,000 | $7 | 4.2 |
| Australia | 25,000 | 2% | $50,000 | $15 | 3.8 |
This sample report highlights the importance of comparing performance across markets. Notice how the US market boasts high website traffic and revenue, while Australia shows significantly lower performance across all metrics. This data indicates a need for strategic adjustments in the Australian market, potentially focusing on improving website engagement, lowering CAC, or enhancing customer satisfaction through localized marketing campaigns.
Case Studies of Successful Global Expansion

Source: thedistrictweekly.com
Successfully expanding a business globally requires meticulous planning and execution, particularly in navigating the complexities of localization and internationalization. Understanding how other companies have achieved this can provide invaluable insights. This section examines several case studies, highlighting their strategies and contributing factors to their global success.
Netflix’s Global Domination Through Localized Content
Netflix’s remarkable global expansion is a prime example of successful internationalization and localization. Initially focused on the US market, Netflix strategically expanded into international markets by offering localized content. This wasn’t simply about translating subtitles; it involved commissioning original programming tailored to specific regional tastes and preferences. For example, Netflix invested heavily in Korean dramas and anime, recognizing their global appeal and local popularity.
Their success stems from a data-driven approach, using viewing data to understand regional preferences and inform content acquisition and creation. Simultaneously, they adapted their user interface and payment options to cater to the specific needs of each market. This multifaceted approach, combining localized content with a flexible platform, enabled Netflix to overcome cultural and technological barriers, leading to significant global market penetration.
Spotify’s Global Music Streaming Strategy
Spotify’s global success demonstrates the importance of adapting to local regulations and preferences. The company successfully navigated complex licensing agreements in different countries, securing the rights to offer diverse music catalogs tailored to regional tastes. Their localized approach extended beyond just music selection. They adapted their user interface and payment methods to suit local markets, offering options that were convenient and culturally appropriate.
Spotify’s algorithm also learns and adapts to individual user preferences, contributing to a personalized experience that resonates globally. Their agile approach to localization and internationalization, coupled with a user-friendly platform, allowed them to rapidly expand into new markets and establish a strong global presence.
IKEA’s Adaptable Furniture and Global Retail Model
IKEA’s global success is a testament to the power of adapting a core product offering to suit diverse cultural contexts. While their core design philosophy remains consistent, IKEA tailors its product lines to reflect local preferences and needs. For example, they offer different furniture sizes and styles to accommodate varying living spaces and cultural norms. Their retail strategy also adapts to local markets, with store layouts and marketing campaigns reflecting local tastes and shopping habits.
Beyond product and marketing, IKEA’s global expansion strategy focused on establishing local supply chains and employing local staff, fostering a sense of community and understanding. This culturally sensitive approach, combined with a strong brand identity and a consistent value proposition, contributed to IKEA’s impressive global growth.
Case Study Summary Table
| Company | Key Localization/Internationalization Strategies | Factors Contributing to Success | Global Market Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Netflix | Localized content (original programming, subtitles, dubbing), adapted user interface and payment options, data-driven approach | Understanding regional preferences, investment in local content, flexible platform | Global market leader in streaming services |
| Spotify | Localized music catalogs, adapted user interface and payment methods, personalized recommendations | Navigating complex licensing agreements, user-friendly platform, agile approach to localization | Global leader in music streaming |
| IKEA | Adapted product lines, localized marketing campaigns, local supply chains and staffing | Cultural sensitivity, strong brand identity, consistent value proposition | Global leader in furniture retail |
Last Recap
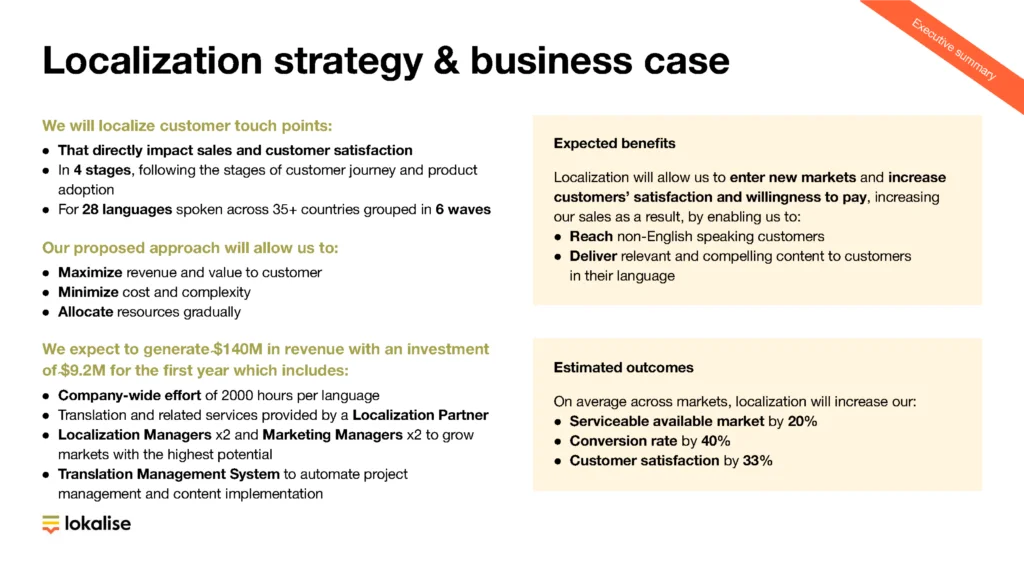
Source: lokalise.com
Expanding your business globally through localization and internationalization isn’t a sprint, it’s a marathon. It demands thorough planning, a deep understanding of your target markets, and a commitment to ongoing adaptation. But the rewards—access to a vastly expanded customer base and increased revenue—are well worth the effort. Remember, success lies in building authentic connections with your international customers by respecting their culture and providing a truly localized experience.
So, embrace the challenge, leverage the strategies Artikeld here, and watch your global customer base flourish!
Essential FAQs
What’s the difference between localization and internationalization?
Internationalization (i18n) is the process of designing and developing a product so it can be easily adapted to different languages and regions without engineering changes. Localization (l10n) is the actual adaptation of the product to a specific target market, including translation, cultural adjustments, and regional settings.
How much does professional translation cost?
Costs vary greatly depending on the volume of text, language pair, and level of expertise required. Get quotes from multiple professional translation services to compare pricing and services.
What are some common legal pitfalls to avoid?
Be aware of differing data privacy regulations (like GDPR), copyright laws, and trademark issues in each target market. Consult with legal professionals specializing in international business law.
How do I measure the success of my internationalization efforts?
Track key performance indicators (KPIs) like website traffic from different regions, conversion rates, customer acquisition costs, and customer satisfaction in each market. Analyze this data to refine your strategies.