
Media Street Price Increase Whats Happening?
Media street price increase is hitting us hard, folks! From the books we love to the movies we binge, everything seems to be getting pricier. This isn’t just about a few extra dollars; it’s a reflection of larger economic forces at play, impacting everything from production costs to distribution networks. Let’s dive into the nitty-gritty and explore what’s behind this rising tide of media expenses.
This price hike isn’t happening in a vacuum. Inflation, supply chain issues, and even the cost of energy are all contributing factors. We’ll examine how these elements are affecting different media types – books, music, movies – and explore the consequences for consumers and the industry as a whole. We’ll also look at how companies are responding, what governments are doing (or not doing), and what the future might hold for our entertainment budgets.
Factors Contributing to Media Street Price Increases
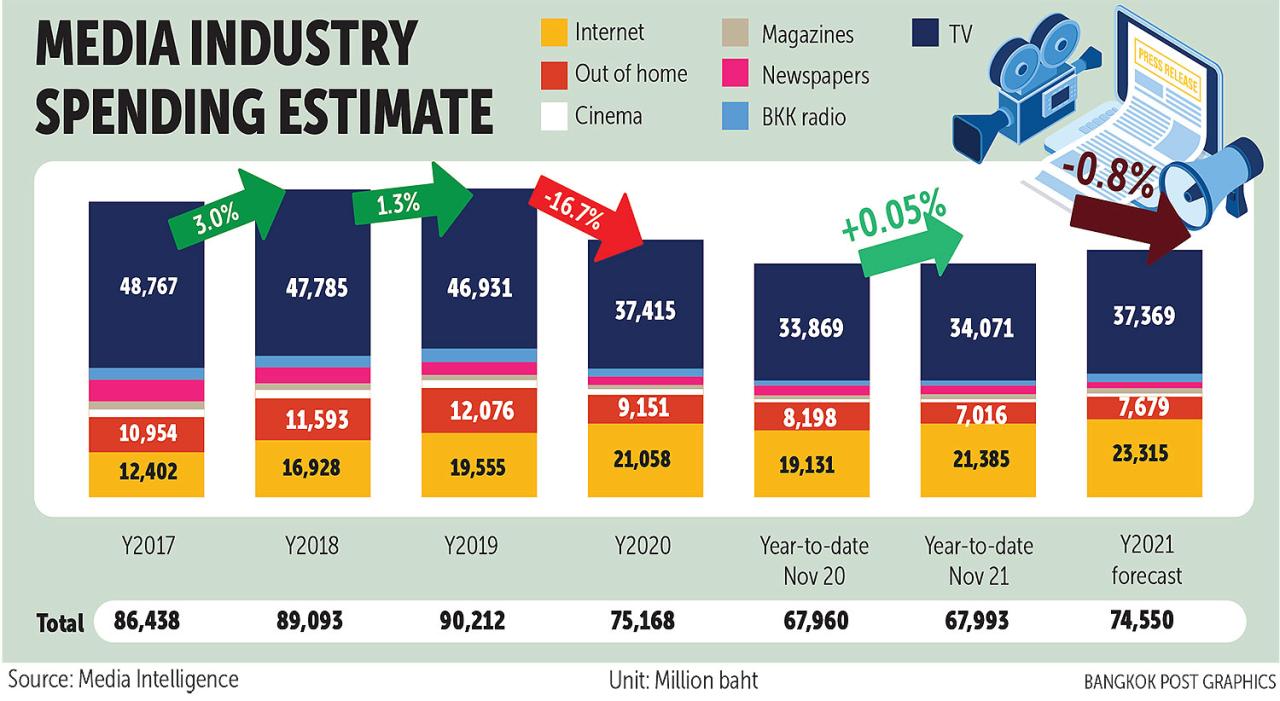
Source: bangkokpost.com
The recent surge in the street prices of various media formats – from books and music to movies and video games – has left many consumers feeling the pinch. This isn’t simply a matter of businesses raising prices arbitrarily; a confluence of factors, primarily economic and logistical, is driving these increases. Understanding these contributing elements is crucial for both consumers and industry professionals alike.
Inflation’s Impact on Media Production Costs
Inflation significantly impacts the cost of producing media. Increased prices for raw materials like paper (for books), plastic (for packaging), and even electricity (for recording studios and printing presses) directly translate to higher production costs. These increased costs are then passed on to consumers in the form of higher retail prices. For example, the rising cost of ink and paper has directly affected the price of printing and binding books, leading to noticeable increases in cover prices.
Similarly, the increased cost of electricity needed to power recording studios has impacted the production budget of music albums.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Media Pricing
Global supply chain disruptions, exacerbated by factors like the pandemic and geopolitical instability, have played a significant role. Delays in the delivery of raw materials, printing components, and distribution logistics all add to the overall cost of getting media products to market. The scarcity of certain materials due to these disruptions further inflates prices. For instance, the shortage of microchips has affected the production of certain gaming consoles, leading to price hikes and longer waiting times for consumers.
Increased Energy Costs and Media Distribution
The rising cost of energy affects every stage of the media supply chain, from manufacturing to distribution. Increased fuel prices directly impact transportation costs, making it more expensive to ship books, CDs, or DVDs to retailers and ultimately to consumers. The energy consumed in data centers for streaming services also contributes to the overall operational costs, which can be reflected in subscription prices or the cost of individual digital purchases.
For example, the cost of transporting a pallet of books across the country has increased significantly due to higher fuel costs, directly impacting the final price.
Raw Material Price Fluctuations and Media Street Prices
The price volatility of raw materials is a major factor. Fluctuations in the price of paper pulp, plastics, and metals used in packaging directly impact the manufacturing costs of media products. These fluctuations are often unpredictable and can lead to sudden and significant price increases. For instance, a sudden surge in the price of oil, a key component in many plastics, can quickly increase the cost of producing CD cases or DVD packaging.
Comparative Price Increases Across Media Types (Past Year), Media street price increase
The following table compares the approximate percentage increase in street prices for different media types over the past year. These figures are estimations based on available market data and may vary depending on specific products and retailers.
| Media Type | Approximate Price Increase (%) | Contributing Factors | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Books (Hardcover) | 5-10% | Paper, printing, shipping | Increased cost of paper pulp and higher transportation costs. |
| Music (Physical Albums) | 7-12% | Manufacturing, packaging, shipping | Higher costs of vinyl production and plastic packaging. |
| Movies (Blu-ray) | 8-15% | Manufacturing, packaging, distribution | Increased costs of disc production and plastic cases. |
| Video Games (Physical Copies) | 10-18% | Manufacturing, packaging, shipping, components | Higher costs of game cartridges and packaging, increased shipping costs. |
Impact of Price Increases on Consumers: Media Street Price Increase
The recent surge in media subscription prices is forcing consumers to re-evaluate their entertainment budgets and consumption habits. This isn’t simply about a few extra dollars; it represents a significant shift in the accessibility and affordability of entertainment for many. The impact ripples across various demographics and leads to some interesting changes in how we consume media.Higher media prices directly affect consumer purchasing habits.
Many individuals will likely reduce their overall spending on media services, perhaps by canceling less-used subscriptions or opting for free, ad-supported alternatives. This could mean less streaming, fewer premium cable channels, and a decreased reliance on paid digital content. The squeeze on disposable income, particularly in the current economic climate, exacerbates this effect.
Shift in Consumer Preference Towards Cheaper Alternatives
The price increases are pushing consumers towards more budget-friendly options. This includes a resurgence in free, ad-supported streaming platforms, increased reliance on public broadcasting, and a greater interest in borrowing media from libraries or friends. The shift is not just about cost; it also involves a re-evaluation of value. Consumers are increasingly scrutinizing the content offered by subscription services, canceling those deemed less valuable for the price.
For example, the rise of free streaming services with a substantial library of content, albeit with advertising, has become a viable and attractive alternative for many.
Demographic Groups Most Affected by Price Increases
Lower-income households and families are disproportionately affected by media price increases. For those already struggling to make ends meet, the added cost of entertainment subscriptions can be a significant burden, forcing difficult choices between essential needs and entertainment. Similarly, students and young adults, often with limited disposable income, are likely to reduce their media consumption or seek out cheaper options.
This contrasts with higher-income individuals who may be less impacted by the price changes, continuing their existing subscription habits with minimal disruption.
Implications for Media Consumption Patterns
The impact on media consumption patterns is multifaceted. We might see a decline in overall media consumption, as individuals cut back on services they can no longer afford. There might also be a shift towards on-demand viewing, as consumers become more selective about what they watch, opting to watch only specific shows or movies rather than maintaining a broad range of subscriptions.
This could lead to less passive consumption and more focused viewing habits. Furthermore, the increased reliance on free, ad-supported services might lead to a higher tolerance for advertising, altering the viewer experience.
Strategies Consumers Might Employ to Mitigate the Impact of Increased Media Costs
The rising cost of media presents a challenge, but consumers can adopt several strategies to manage their expenses. Careful consideration of subscription services is key.
- Regularly review subscriptions: Cancel any services that are not regularly used or offer poor value for the price.
- Share subscriptions: Split the cost of streaming services with family or friends.
- Explore free alternatives: Utilize free, ad-supported streaming platforms and public broadcasting options.
- Utilize libraries and borrowing: Borrow movies and books from libraries or friends to reduce purchase costs.
- Prioritize spending: Focus spending on the media services that offer the most value and enjoyment.
Industry Responses to Price Increases
The recent surge in media street prices has forced the industry to re-evaluate its strategies, prompting a diverse range of responses. Some companies have opted for aggressive price hikes, while others have focused on enhancing value propositions or exploring alternative revenue models. The effectiveness of these strategies varies greatly depending on factors like brand loyalty, audience demographics, and the specific media being offered.
Pricing Strategies of Different Media Companies
Media companies are employing a variety of pricing strategies in response to rising costs. Some, particularly those with strong brand recognition and loyal subscriber bases, have implemented relatively straightforward price increases, relying on the existing customer base to absorb the cost. Others, especially those targeting price-sensitive consumers, have adopted a more nuanced approach, offering tiered subscription packages or introducing cheaper, ad-supported options alongside premium, ad-free services.
For example, Netflix’s introduction of a cheaper, ad-supported plan reflects this strategy, allowing them to retain customers while increasing overall revenue. Conversely, some smaller, niche media outlets have opted to maintain their prices, potentially accepting lower profit margins or seeking alternative funding sources. This strategy is riskier but can help maintain customer loyalty in competitive markets.
Effectiveness of Marketing Campaigns During Price Increases
The success of marketing campaigns during price increases hinges on transparency and value communication. Effective campaigns emphasize the increased value offered at the new price point, highlighting improvements in content quality, service features, or exclusive access. For example, a streaming service might advertise the addition of high-profile original programming or an improved user interface to justify a price increase.
Conversely, campaigns that attempt to downplay or ignore the price hike are often less successful and may even damage consumer trust. Companies are using data analytics to target specific customer segments with tailored messaging, focusing on the benefits most relevant to each group. This approach allows for more efficient resource allocation and potentially higher conversion rates.
Comparison of Media Distribution Models and Susceptibility to Price Increases
Different media distribution models exhibit varying degrees of susceptibility to price increases. Traditional broadcast television, for instance, is relatively less vulnerable due to its established advertising revenue streams and broad audience reach. However, streaming services, reliant on subscription fees, are more directly impacted by price sensitivity. Digital downloads and physical media sales, already facing competition from streaming, are particularly vulnerable, potentially requiring innovative pricing models like bundled offers or tiered access to mitigate the impact of price increases.
Media street prices are skyrocketing, making it harder than ever to get quality content. But if you’re serious about building an audience, you need to explore other avenues, like mastering video marketing. Check out this great guide on getting it on with YouTube to learn how to leverage the platform effectively. Ultimately, understanding YouTube’s algorithm can help offset those rising media costs and boost your reach.
The shift towards subscription-based models, while offering stability, also increases vulnerability to customer churn if price increases are not carefully managed.
Adaptation of Subscription Services to Increased Production Costs
Subscription services are responding to increased production costs through a combination of strategies. Price adjustments are a common response, often accompanied by efforts to enhance the value proposition, such as adding new content, improving user experience, or offering exclusive perks to subscribers. Some services are also exploring ways to optimize their production processes, using more efficient technologies and streamlining workflows to reduce operational costs.
Others are diversifying their revenue streams by integrating advertising, offering premium add-on features, or exploring partnerships with other businesses. For example, many streaming services now offer bundled packages with other services, like mobile phone plans or internet access, to reduce price sensitivity.
Innovative Approaches to Maintain Profitability
Media companies are employing various innovative approaches to maintain profitability in the face of rising costs. This includes leveraging data analytics to personalize content recommendations, enhancing customer engagement through interactive features, and expanding into new markets or demographics. Some companies are exploring alternative funding models, such as crowdfunding or patronage programs, to supplement subscription revenue. Others are focusing on creating more efficient production pipelines, using technologies like AI to automate tasks and reduce labor costs.
The development of more efficient distribution networks and targeted advertising strategies are also proving effective in optimizing profitability.
Government Regulations and Media Pricing
Government policies play a significant, often unseen, role in shaping the cost of media products and services. These policies range from direct price controls (rare in the modern media landscape) to indirect influences through taxation, antitrust regulations, and subsidies. Understanding this regulatory landscape is crucial to comprehending the recent price increases across various media platforms.
The Impact of Antitrust Laws on Media Pricing
Antitrust laws, designed to prevent monopolies and promote competition, significantly influence media pricing. These laws aim to ensure a level playing field, preventing dominant companies from exploiting their market power to inflate prices arbitrarily. For example, the scrutiny faced by large tech companies like Google and Facebook regarding their market dominance often leads to investigations and potential fines for anti-competitive practices that could artificially inflate advertising costs, ultimately affecting the price consumers pay for media services.
The enforcement of antitrust laws can vary widely across jurisdictions, with some countries having more robust regulatory frameworks than others. This difference directly affects the level of competition and consequently, the price of media products. A lack of effective enforcement can lead to higher prices for consumers due to reduced competition.
Government Interventions to Alleviate Rising Media Costs
Several government interventions could potentially alleviate the burden of rising media costs on consumers. Subsidies for public broadcasting or independent media outlets can help ensure the availability of diverse and affordable content. Regulatory measures that promote competition, such as breaking up media monopolies or facilitating the entry of new players into the market, can also help lower prices.
Furthermore, governments can implement policies that encourage the development and adoption of affordable media technologies, potentially reducing the cost of access for consumers. For instance, initiatives supporting broadband infrastructure development directly impact the affordability of streaming services and online media consumption.
Tax Policies and Media Affordability
Tax policies can significantly impact the affordability of media products. Sales taxes, for instance, directly increase the final price paid by consumers. Conversely, tax breaks or exemptions for certain media products (e.g., educational materials) can make them more accessible. The introduction or removal of taxes on digital services, such as streaming subscriptions, can also influence consumer spending patterns and the overall cost of media access.
Governments may also choose to levy taxes on media companies themselves, which can indirectly impact prices through increased production costs. This complex interplay of taxes affects both the supply and demand sides of the media market, ultimately influencing prices.
Regulatory Landscape for Media Pricing in Different Countries
| Country | Antitrust Enforcement | Media Subsidies | Tax Policies on Media |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Relatively strong, with ongoing scrutiny of large tech companies | Limited direct subsidies, mostly focused on public broadcasting | Sales tax varies by state; digital services taxation is evolving |
| European Union | Strong emphasis on competition policy, with significant regulatory power | Subsidies for public broadcasters and cultural initiatives are common | VAT applies to most media products; specific digital service taxes are being implemented |
| Canada | Moderate antitrust enforcement; focus on promoting Canadian content | Significant subsidies for Canadian media production and broadcasting | GST applies to most media products; specific digital service taxes are under consideration |
| China | Strong government control over media; limited private sector competition | Government funding dominates media landscape | Taxation policies are largely dictated by government priorities |
Long-Term Implications of the Trend

Source: slideplayer.com
The consistent upward pressure on media prices presents a complex and multifaceted challenge with significant long-term implications for consumers, creators, and the industry as a whole. Sustained price increases risk fundamentally altering the media landscape, impacting accessibility, diversity, and innovation in unforeseen ways.The potential consequences of continuously rising media prices are far-reaching and interconnected. A cascading effect could be observed, impacting not only individual consumption habits but also the broader creative ecosystem and the very structure of media industries.
Impact on Media Diversity and Accessibility
Increased media costs directly limit access for many consumers. Higher subscription fees and pay-per-view options could create a digital divide, excluding lower-income households and those in underserved communities from participating in the broader cultural conversation. This could lead to a homogenization of media content, with providers prioritizing commercially viable projects over niche or experimental works. The resulting lack of diverse voices and perspectives could stifle creativity and limit the range of narratives available to audiences.
For example, independent filmmakers and smaller news organizations might struggle to compete, leading to a decrease in diverse viewpoints and perspectives.
Implications for Media Innovation and Creativity
While some argue that higher prices incentivize higher quality production, the reality is more nuanced. Sustained price increases could stifle innovation by reducing the risk tolerance of media companies. They may become less willing to invest in experimental projects or unproven talent, opting instead for safer, more predictable content that maximizes returns on investment. This could lead to a decline in originality and a lack of fresh perspectives, ultimately diminishing the quality and impact of media content.
For instance, the increasing cost of producing high-quality animation could discourage studios from taking risks on original stories in favor of sequels or adaptations.
Effects on the Future of Media Industries
The long-term effects on media industries could include consolidation and monopolization. As smaller players struggle to compete with rising costs, larger corporations may acquire them, leading to a less competitive market. This could result in less choice for consumers and potentially higher prices in the long run. The music industry, for example, has seen significant consolidation over the past few decades, with a few major labels controlling a large share of the market.
Similar trends could play out in other media sectors. Additionally, the increasing cost of production could lead to a shift in business models, with a greater emphasis on advertising revenue or subscription services.
Technological Advancements as a Counterbalance
Technological advancements hold the potential to mitigate some of the negative impacts of rising media costs. For example, advancements in streaming technology could lead to more efficient content delivery, reducing production and distribution costs. Similarly, improvements in artificial intelligence could automate certain aspects of content creation, making it more affordable. However, the extent to which technology can offset rising costs remains uncertain.
The development and adoption of these technologies may be slow, and their benefits may not be evenly distributed across the media landscape. For example, while AI could assist in tasks like video editing, it is unlikely to fully replace human creativity and storytelling skills.
Outcome Summary

Source: api.news
The media street price increase isn’t just a temporary blip; it’s a significant trend with far-reaching implications. From altering consumer habits to forcing industry innovation, the ripple effects are undeniable. While the future remains uncertain, understanding the factors driving these price hikes is crucial for both consumers and industry players alike. Staying informed and adapting to these changes will be key to navigating this new landscape of entertainment costs.
FAQ Summary
Will prices continue to rise?
It’s difficult to say for certain. Continued inflation and supply chain instability could fuel further increases, but technological advancements and industry innovation could potentially offset some of the costs.
Are digital media affected?
Yes, even digital media is susceptible. Increased server costs, bandwidth expenses, and the cost of developing and maintaining digital platforms all contribute to the final price.
What can I do to save money?
Consider borrowing books from libraries, exploring streaming services with cheaper plans, buying used media, and taking advantage of sales and discounts.
