
Speed Matters to Google SEO & UX
Speed matters to Google; it’s not just a catchy phrase, it’s the bedrock of a successful online presence. Google’s algorithms prioritize fast-loading websites, rewarding them with higher search rankings and increased visibility. But the benefits extend far beyond . A snappy website enhances user experience, leading to improved engagement and ultimately, a healthier bottom line. This post dives deep into why speed is crucial, how it affects both Google and your users, and the practical steps you can take to optimize your site for speed.
We’ll explore the technical aspects of website optimization, from image compression to leveraging CDNs, and delve into the various tools available to measure and improve your website’s performance. Whether you’re running an e-commerce store, a blog, or a news site, understanding and implementing speed optimization strategies is no longer optional – it’s essential for survival in today’s competitive digital landscape.
Get ready to learn how to make your website a speed demon!
Website Loading Speed & User Experience
Website speed isn’t just a technical detail; it’s a crucial factor directly impacting user experience and, ultimately, your business success. A slow-loading website can frustrate visitors, leading them to abandon your site before they even see what you have to offer. Conversely, a fast website creates a positive first impression and encourages users to explore further. The relationship between speed and user experience is undeniable, and understanding this connection is paramount for any online business.
The impact of website speed on user experience is multifaceted and significantly affects key engagement metrics. Let’s delve into the specific ways slow loading times negatively impact user interactions and business outcomes.
Website Speed and Bounce Rate
A high bounce rate signifies a significant number of visitors leaving your website after viewing only one page. Slow loading speeds are a major contributor to this. Imagine arriving at a website and facing a frustratingly long wait – it’s natural to lose patience and click away. Studies consistently show a strong correlation between slow load times and increased bounce rates.
A delay of even a few seconds can noticeably increase the likelihood of users abandoning your site. For example, a study by Google found that 53% of mobile site visits are abandoned if a page takes longer than three seconds to load. This highlights the critical need for optimization to minimize this crucial metric.
Slow Loading Times and User Engagement Metrics
Slow loading times significantly impact key engagement metrics like “time on site” and “pages per visit.” When a website loads slowly, users spend less time browsing and are less likely to navigate to other pages. This directly translates to reduced engagement and missed opportunities for conversions. For instance, a user might be interested in learning more about your product, but if the product page takes too long to load, they might give up before they can access the information.
This loss of engagement directly affects your bottom line.
User Experience Comparison: Fast vs. Slow Loading Website
The difference in user experience between a fast and a slow loading website is stark. A fast website provides a seamless and enjoyable experience, while a slow one creates frustration and a negative perception of your brand.
| Speed | User Feeling | Actions Taken | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fast (under 2 seconds) | Positive, impressed, engaged | Browses multiple pages, interacts with content, makes a purchase | High conversion rates, positive brand perception, increased customer loyalty |
| Slow (over 5 seconds) | Frustrated, impatient, annoyed | Leaves the website, doesn’t interact with content, doesn’t make a purchase | Low conversion rates, negative brand perception, lost revenue |
Google’s Search Algorithm & Speed
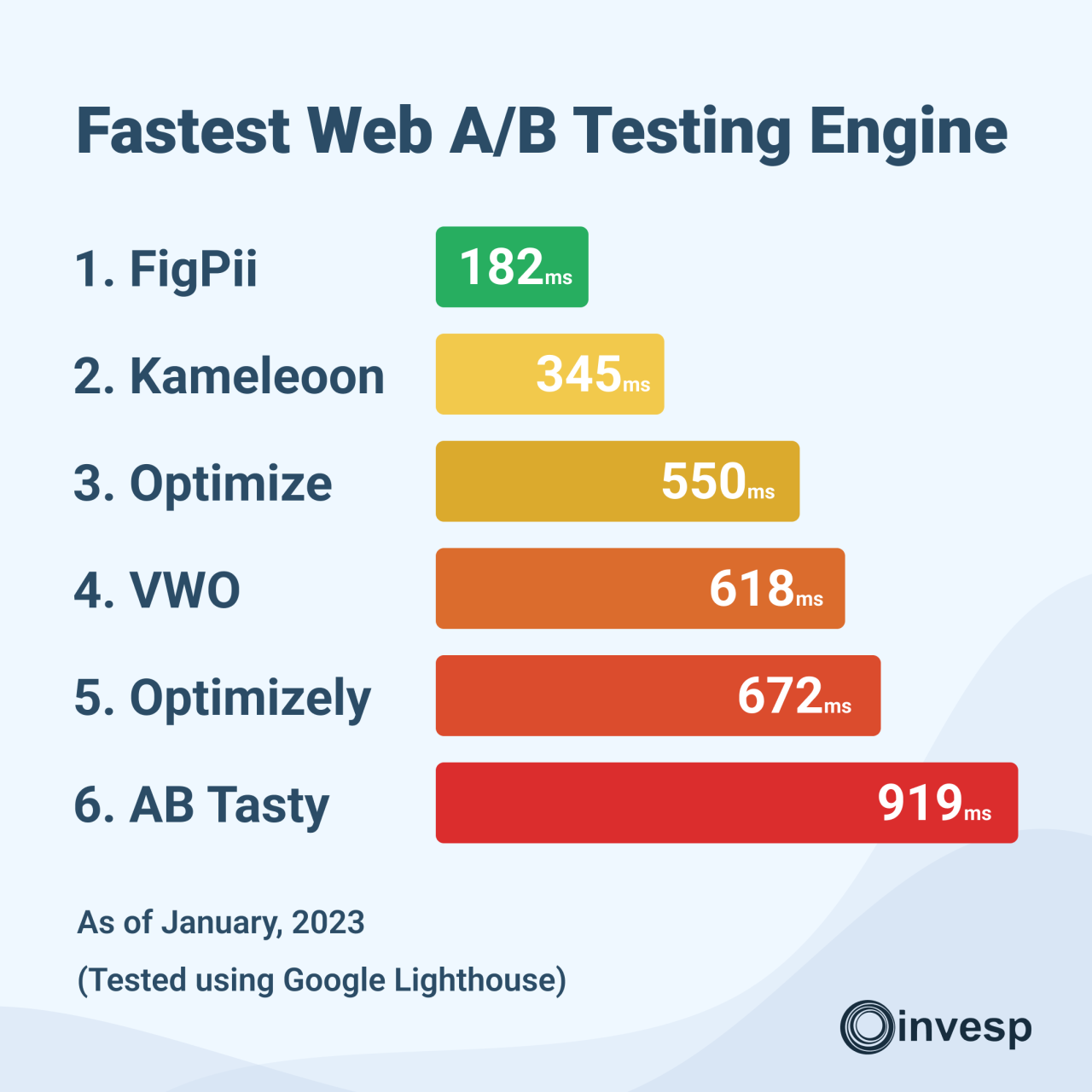
Source: invespcro.com
Google’s search algorithm is incredibly complex, but one key factor consistently influencing search rankings is website speed. A fast-loading website is not just a matter of user experience; it’s a significant ranking signal for Google, impacting visibility and ultimately, your website’s success. This means optimizing your site for speed isn’t optional – it’s crucial for achieving higher search rankings.Google prioritizes fast-loading websites because speed directly correlates with user satisfaction.
A slow website frustrates users, leading to higher bounce rates and shorter session durations. Google’s algorithms interpret these negative user signals as an indication of a poor-quality website, pushing it lower in search results. This prioritization is reinforced through several key components of Google’s ranking system.
Core Web Vitals’ Influence on Search Rankings
Core Web Vitals are a set of metrics that Google uses to measure the user experience of a website. These metrics directly impact search rankings. Specifically, they assess aspects like Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), and First Input Delay (FID). A website with poor Core Web Vitals scores will likely rank lower than a site with excellent scores, all other factors being equal.
Google’s Search Console provides tools to monitor these metrics and identify areas for improvement. Addressing issues like slow image loading, inefficient JavaScript execution, and render-blocking resources directly improves these vital scores and boosts search ranking potential.
Examples of Google’s Penalties for Slow Websites
While Google doesn’t explicitly “penalize” websites solely for slow loading speeds, the indirect consequences are significant. A slow website suffers from lower rankings due to poor user experience signals. This can lead to reduced organic traffic, impacting visibility and revenue, particularly for businesses relying on online sales. For example, an e-commerce site experiencing slow page load times might see a significant drop in conversions as customers abandon their carts due to frustration.
Similarly, a news site with slow loading pages might lose readers to competitors who offer a faster, more responsive experience. The effect isn’t a direct penalty in the form of a manual action, but rather a natural consequence of the algorithm’s focus on user experience. This makes optimization crucial for maintaining a strong search presence.
Speed’s Importance Across Different Website Types
The importance of website speed varies slightly depending on the type of website. For e-commerce sites, speed is paramount; a slow checkout process can directly impact sales conversions. Customers are less likely to complete a purchase on a slow website, resulting in lost revenue. News sites also benefit greatly from fast loading times; readers are less likely to wait for a slow page to load, potentially turning to a competitor’s faster site for breaking news.
Blogs, while less directly impacted by speed than e-commerce sites, still benefit from improved user experience and potentially higher engagement if pages load quickly. A fast-loading blog encourages readers to browse multiple articles, increasing overall time spent on the site. In essence, while the specific impact might vary, prioritizing speed is beneficial across all website types.
Technical Aspects of Website Speed Optimization

Source: creativethinksmedia.com
Website speed isn’t just about user experience; it’s a critical factor impacting your search engine ranking and overall business success. Technical optimization is the cornerstone of a fast-loading website, focusing on the underlying code and infrastructure. Ignoring these aspects can severely hamper performance, no matter how sleek your design is.
Key Factors Contributing to Slow Website Loading Times
Three major technical culprits often slow down websites: inefficient code, unoptimized images, and a lack of caching. Inefficient code, such as bloated JavaScript or poorly written CSS, can significantly increase page load times. Large, uncompressed images are another common bottleneck, consuming considerable bandwidth. Finally, the absence of caching mechanisms forces the server to reprocess requests for each user, increasing server load and response times.
Addressing these issues is vital for improving website performance.
Caching Mechanisms for Improved Website Speed
Caching involves storing frequently accessed data closer to the user, reducing the server’s workload and speeding up delivery. Browser caching stores assets (images, CSS, JavaScript) locally on the user’s device, preventing repeated downloads. Server-side caching stores generated content on the server, avoiding redundant processing. A well-implemented caching strategy significantly reduces server requests and response times, leading to a noticeably faster website.
For example, a website using aggressive caching might see a 50% reduction in server load during peak hours, leading to a smoother user experience and faster page load times for everyone.
Benefits of Using a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a geographically distributed group of servers that deliver content to users based on their location. This significantly reduces latency, as users access content from a server closer to them. CDNs are particularly beneficial for websites with a global audience, ensuring fast loading times regardless of the user’s location. Furthermore, CDNs often include built-in caching and security features, enhancing both speed and security.
Imagine a website with a global reach – a CDN can reduce loading times by an average of 50% or more, depending on the geographic distribution of users and the server locations.
Optimizing Images for Web Performance
Optimizing images is crucial for website speed. Follow these steps for best results:
- Choose the right format: Use JPEG for photographs and PNG for graphics with transparency. WebP offers superior compression for both.
- Compress images: Use tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim to reduce file size without significant quality loss. Aim for a balance between image quality and file size.
- Resize images appropriately: Don’t upload images larger than necessary. Resize images to the exact dimensions required on your website.
- Use responsive images: Implement responsive images using the `
` element or `srcset` attribute to serve different image sizes based on the user’s device. - Use lazy loading: Only load images as they are needed, improving initial page load time. This is especially beneficial for images below the fold.
Measuring and Improving Website Speed
Website speed is crucial for user experience and . A slow-loading website can lead to high bounce rates, lost conversions, and lower search engine rankings. Understanding how to measure and improve your site’s speed is therefore essential for online success. This section delves into the practical aspects of website speed optimization, providing tools, interpretations, and best practices.
Website Speed Testing Tools
Several tools are available to measure your website’s loading speed. These tools offer valuable insights into various performance metrics, helping you identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement. Choosing the right tool depends on your specific needs and technical expertise. Some popular options include Google PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, WebPageTest, and Pingdom Website Speed Test. These tools analyze various aspects of your website’s performance, such as Time to First Byte (TTFB), First Contentful Paint (FCP), Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), and Total Blocking Time (TBT).
Interpreting Website Speed Test Results
Understanding the results from speed testing tools is crucial for effective optimization. Each tool provides a report detailing various metrics. For example, a high TTFB indicates a slow server response, while a high LCP suggests slow loading of the main content. A high CLS score points to visual instability, causing a poor user experience. Interpreting these metrics helps pinpoint the specific areas needing attention.
Consider using a combination of tools to get a more comprehensive view of your website’s performance across different locations and devices. Pay close attention to the recommendations provided by these tools; they often suggest specific improvements tailored to your website’s issues.
Best Practices for Improving Website Speed
Optimizing your website’s speed involves a multi-faceted approach. The following best practices can significantly improve your site’s performance:
- Optimize Images: Compress images using tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim to reduce file size without significant quality loss. Use appropriate image formats (WebP for superior compression) and dimensions.
- Leverage Browser Caching: Configure your server to enable browser caching, allowing browsers to store static assets (images, CSS, JavaScript) locally, reducing subsequent load times.
- Minify CSS and JavaScript: Remove unnecessary characters from your CSS and JavaScript files to reduce their size, improving download speed.
- Enable GZIP Compression: Compress your website’s content using GZIP to reduce the amount of data transferred, speeding up loading times.
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN): Distribute your website’s content across multiple servers globally, reducing latency for users in different locations.
- Optimize Database Queries: Ensure your database queries are efficient and optimized to avoid slowdowns.
- Reduce HTTP Requests: Combine CSS and JavaScript files, and use CSS sprites to reduce the number of HTTP requests your browser needs to make.
- Choose a Fast Web Hosting Provider: A reliable and fast hosting provider is fundamental for optimal website performance.
Visual Representation of Optimization Techniques’ Impact
Imagine a bar chart. The X-axis represents different optimization techniques (e.g., image optimization, CSS minification, CDN implementation). The Y-axis represents page load time in seconds. Initially, a tall bar represents the original page load time (e.g., 5 seconds). After implementing image optimization, the bar shortens to, say, 4 seconds.
Further implementing CSS minification reduces it to 3.5 seconds. Finally, using a CDN might reduce it to 2 seconds. This visual demonstrates the cumulative effect of various optimization techniques in reducing page load time. Each bar represents a stage of optimization, clearly showing the progressive improvement in speed. The final bar, representing the optimized page load time, is significantly shorter than the initial bar, illustrating the substantial impact of implementing these techniques.
The difference between each bar visually represents the improvement achieved by each specific optimization method. For instance, the difference between the initial bar and the bar after image optimization clearly shows the positive impact of optimizing images.
Mobile Website Speed

Source: we3labs.com
In today’s mobile-first world, website speed on mobile devices is no longer a mere convenience; it’s a critical factor for success. Google’s mobile-first indexing means that the mobile version of your website is the primary version Google uses to rank your site. A slow mobile site translates directly to lower rankings, reduced visibility, and ultimately, fewer customers. This section dives into the specifics of optimizing your mobile site for speed, considering the unique challenges and opportunities presented by this platform.
Google’s mobile-first indexing prioritizes the mobile experience, meaning a slow mobile site will negatively impact your search engine rankings. A fast-loading mobile website is essential for a positive user experience, leading to increased engagement, lower bounce rates, and higher conversion rates. Conversely, a slow mobile site frustrates users, leading them to abandon your site and seek information elsewhere. The impact on your bottom line is significant.
Google prioritizes speed; a slow website is a penalized website. This is especially crucial when you’re trying to boost your channel’s visibility, which is why understanding how to optimize your videos is key. Check out this guide on getting it on with YouTube to learn how to improve your video loading times. Ultimately, faster loading times mean better search rankings, proving once again that speed matters to Google.
Mobile Versus Desktop Optimization Challenges
Optimizing for mobile presents a unique set of challenges compared to desktop optimization. Mobile devices typically have less processing power, slower internet connections (especially on 3G/4G networks), and smaller screens. These limitations necessitate a different approach to optimization. While desktop optimization often focuses on minimizing HTTP requests and optimizing images, mobile optimization requires a more holistic approach, addressing issues like data compression, efficient JavaScript execution, and the impact of responsive design.
For example, a large, high-resolution image might load quickly on a desktop but take an unacceptable amount of time on a mobile device with a slower connection.
Responsive Design and Mobile Speed
Responsive design, where a single website adapts to different screen sizes, is crucial for mobile speed. A well-implemented responsive design avoids the need for separate mobile and desktop websites, streamlining the user experience and simplifying optimization efforts. However, a poorly implemented responsive design can actually
-hinder* mobile speed. For example, using oversized images or inefficient CSS/JavaScript can negatively impact loading times, even with a responsive design.
Therefore, careful attention to code efficiency and image optimization is crucial regardless of whether a responsive design is used. A well-structured responsive site uses efficient code and optimized assets, leading to faster loading times across all devices. Conversely, a poorly structured responsive site can lead to slow loading times due to inefficient code or oversized assets.
Mobile Website Optimization Best Practices, Speed matters to google
Optimizing your mobile website requires a multi-pronged approach. The following checklist Artikels key best practices to ensure a fast and efficient mobile experience:
Prioritizing mobile optimization is paramount for success in today’s mobile-centric world. These practices, when implemented correctly, contribute significantly to a positive user experience and improved search engine rankings.
- Minimize HTTP Requests: Reduce the number of files your website needs to load by combining CSS and JavaScript files and using CSS sprites for icons.
- Optimize Images: Compress images using tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim to reduce file size without significant loss of quality. Use appropriate image formats (WebP for best results) and sizes for different screen resolutions.
- Leverage Browser Caching: Configure your server to enable browser caching, so the browser can store frequently accessed files locally, reducing loading times on subsequent visits.
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN): A CDN distributes your website’s content across multiple servers globally, reducing latency for users in different locations. This is especially beneficial for mobile users who may have slower or less reliable connections.
- Minify CSS and JavaScript: Remove unnecessary characters (whitespace, comments) from your CSS and JavaScript files to reduce their size and improve loading times.
- Defer Loading of Non-Critical Resources: Delay the loading of resources that aren’t essential for the initial page view, such as images or videos below the fold, to improve initial page load speed.
- Use Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP): While not always necessary, AMP can significantly improve the loading speed of news articles and other content-heavy pages. However, it requires adhering to AMP’s specific specifications.
- Test Regularly: Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights and GTmetrix to regularly test your mobile website’s speed and identify areas for improvement.
Last Word
In short, prioritizing website speed isn’t just about pleasing Google’s algorithm; it’s about creating a positive user experience that drives engagement and boosts your business. By understanding the technical aspects of speed optimization, utilizing available tools, and consistently implementing best practices, you can significantly improve your website’s performance, leading to higher rankings, increased user satisfaction, and ultimately, greater success. So, ditch the slow loading times and embrace the speed! Your website (and your bottom line) will thank you.
FAQ Guide: Speed Matters To Google
What are Core Web Vitals?
Core Web Vitals are a set of metrics Google uses to evaluate a website’s user experience based on loading speed, interactivity, and visual stability.
How does Google penalize slow websites?
Google doesn’t explicitly “penalize” slow websites with a direct ranking drop. However, slow sites rank lower because they provide a poor user experience, which is a major ranking factor.
Is mobile speed more important than desktop speed?
Given Google’s mobile-first indexing, mobile speed is arguably
-more* important. Google primarily crawls and indexes the mobile version of your site.
What’s the difference between caching and a CDN?
Caching stores website data locally to reduce server load. A CDN distributes website content across multiple servers globally, reducing latency for users in different locations.
